The 3.8% net investment income tax (NIIT) is an additional tax that applies to some higher-income taxpayers on top of capital gains tax or ordinary income tax. Fortunately, there are strategies you can use to soften the blow of the NIIT.
You’re potentially liable for the NIIT if your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) exceeds $200,000 ($250,000 for joint filers and qualifying widows or widowers; $125,000 for married taxpayers filing separately). Generally, MAGI is the same as adjusted gross income. However, it may be higher if you have foreign earned income and certain foreign investments.
The NIIT is calculated by multiplying 3.8% by the lesser of:
1) net investment income (NII), or
2) the amount by which MAGI exceeds the applicable threshold.
For example, if you’re single with $250,000 in MAGI and $75,000 in NII, your MAGI will exceed the $200,000 threshold for singles by $50,000, which is less than your NII. So, your NIIT will be 3.8% × $50,000, which equals $1,900.
But if your MAGI instead is $300,000, your NIIT will be 3.8% × $75,000, which equals $2,850. This is because your $75,000 NII is less than the $100,000 amount by which your MAGI will exceed the $200,000 threshold.
NII generally includes net income from taxable interest, dividends, capital gains, rents, royalties and passive business activities. Several types of income are excluded from NII, such as wages, most nonpassive business income, retirement plan distributions and Social Security benefits. Also excluded are alimony and nontaxable gain on the sale of a personal residence.
Given the way the NIIT is calculated, you can reduce or defer the tax by reducing either your MAGI or your NII. Consider:
You also might be able to transfer — either directly or in trust — assets that generate investment income to lower-income family members who aren’t subject to the NIIT. With this strategy, though, be careful not to inadvertently trigger NIIT because of the transfer. For example, trusts have a dramatically lower income threshold level at which NIIT applies.
If you own rental real estate, talk to your tax advisors about how you can avoid NIIT and obtain other tax benefits by qualifying as a materially participating “real estate professional.”
If you hold interests in pass-through entities — such as partnerships, limited liability companies and S corporations — it’s important to consider the interplay between the NIIT and other taxes. For instance, it may be possible to avoid the NIIT by increasing your level of participation to convert a pass-through investment from passive to nonpassive. But in some cases, doing so may also trigger self-employment (SE) or payroll taxes, so it’s important to weigh the NIIT savings against the potential SE or payroll tax costs.
There are many potential strategies for reducing or deferring NIIT, but it’s important to consult with your tax advisor before you implement them. Tax reduction is an important objective, so long as it doesn’t come at the expense of prudent investment decision-making.
© 2023
We’ve closed another year marked by economic uncertainties, and one constant remains—the potential to enhance your company’s financial health by strategically managing your tax obligations. Below, we outline practical and timely strategies tailored for business owners looking to navigate the intricate landscape of tax planning.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) imposed a $10,000 cap on federal income tax deductions for state and local taxes (SALT). Over 30 states, including California, have implemented “workaround” measures benefiting PTE owners to counter this. These provisions allow partnerships, LLCs, and S corporations to pay entity-level state tax, providing owners with corresponding benefits, such as tax credits or deductions. This strategy lets your business bypass the SALT limit, resulting in potential federal business expense deductions.
Cash balance retirement plans are making a comeback, especially for businesses with high-earning individuals who consistently hit their 401(k) limits. These plans offer a unique fusion of defined contribution and defined benefit plans, allowing businesses to claim substantial deductions for contributions.
Remember, under the original SECURE Act, businesses have until their federal filing deadline (including extensions) to set up a cash balance plan. But here’s the practical insight: it takes some time to get everything in order—documents, contribution calculations, and administrative tasks. So, it’s wise to kickstart the process sooner rather than later.
This strategy helps secure your financial future and offers a valuable tax advantage for your business.
Are you using the cash method for income tax reporting? Consider accelerating year-end deductions in December and deferring income until January to optimize your 2023 income. For instance, pay bills and employee bonuses for 2023 before year-end and stock up on supplies to accelerate deductions. Conversely, if higher profits are anticipated in the upcoming year, consider the opposite approach—accelerate income and postpone deductions to maximize their value. Consider the impact on your Qualified Business Income (QBI) deduction, especially if your business operates as a pass-through entity.
A cornerstone of the 2017 tax reform, the QBI deduction for pass-through entities allows owners to claim up to 20% of their QBI, subject to specific limitations. Manage your taxable income wisely, as accelerated depreciation and certain tax breaks tied to taxable income can affect your QBI and subsequent deductions.
Seize the opportunity for first-year bonus depreciation for qualified property acquired and placed in service in 2023. While the benefit gradually diminishes, it remains at 80% for this tax year. Prioritize using IRC Section 179 expensing election for asset purchases, enabling you to deduct 100% of the purchase price for eligible assets. Be aware of the $1.16 million maximum deduction and plan strategically to maximize this tax-saving tool.
Explore the 100% federal income tax gain exclusion for eligible sales of Qualified Small Business Corporation (QSBC) stock acquired after September 27, 2010. Hold QSBC shares for over five years to qualify for the gain exclusion. Planning is crucial to secure this exclusion privilege.
Employing family members can be a strategic move to reduce overall tax liability. Deduct wages and benefits, including medical benefits, paid to family employees, reducing self-employment tax liability. Wages paid to children under 18 are not subject to federal employment taxes, providing potential tax savings.
Remember, seemingly minor tax decisions may have significant consequences. Please consult with us to ensure your business makes informed year-end tax planning moves that align with your goals.
As the end of the tax year approaches, it’s essential to consider strategies to minimize your 2023 federal tax liability. The current landscape presents challenges with market volatility, persistent high-interest rates, and notable adjustments to retirement planning regulations. Despite this uncertainty, there is still an opportunity to implement year-end tax planning techniques to reduce your tax bill. Whether you are contemplating investment decisions, charitable contributions, or estate planning, there are practical strategies to optimize your tax plan.
With a standard deduction of $13,850 for single filers, $27,700 for married couples filing jointly, and $20,800 for heads of households in 2023, assessing your itemized deductions is crucial. Consider strategically timing your itemized deduction items by “bunching” them to exceed the standard deduction every other year. This approach can help lower your tax bill this year, and in the following year, you can take advantage of the increased standard deduction to account for inflation.
Potential candidates for itemized deductions include:
It’s worth noting the possibility of future changes to the value of itemized deductions, emphasizing the importance of maximizing these deductions while current regulations permit.
Effectively managing your investment portfolio can influence your tax liability. Consider the strategic sale of appreciated securities held for over 12 months in 2023, leveraging the favorable 15% federal income tax rate on long-term capital gains. It’s crucial to remember that this rate can increase to 20% for individuals with higher income levels. Equally important is evaluating stocks valued below your initial investment (tax basis). Realizing capital losses this year could offset various gains, including short-term capital gains taxed at ordinary income rates. Always be aware of the wash sale rules before reacquiring recently sold or purchased stocks. This approach allows you to navigate the complexities of the market while optimizing your tax position.
Embrace unique avenues for philanthropy tailored to your preferences:
Safeguard a portion or all of your retirement savings from potential tax rate increases by converting traditional IRAs into Roth accounts. While you’ll incur taxes on the conversion as if it were a traditional IRA distribution, this approach is most beneficial when anticipating remaining in the same or higher tax bracket during retirement. Notably, the current tax impact from conversion may be a small price to pay for evading potentially higher future tax rates on post-conversion earnings. Additionally, the flexibility exists to convert varying amounts over several years, allowing you to tailor the strategy to your circumstances.
If concerns arise about a potentially taxable estate, leverage the annual gift tax exclusion as an effortless method to reduce your taxable estate. In 2023, seize the opportunity to make annual exclusion gifts up to $17,000 per donee, with no limitations on the number of donees. The joint annual exclusion gift limit for couples reaches $34,000 per donee. These tax-free gifts don’t impact your lifetime gifting exemption, providing an effective means to manage your estate’s tax implications.
Homeowners investing in energy-efficient improvements can claim an Energy Efficient Home Improvement Credit, covering up to 30% of qualified expenses, capped at $1,200 annually for energy property costs and an additional $2,000 for qualified heat pumps. Ensure compliance with energy.gov guidelines to include expenses related to doors, windows, air conditioning, and insulation materials. Additionally, explore Residential Clean Energy Credits for qualifying expenses related to solar and alternative energy sources, offering potential tax advantages for environmentally conscious choices.
Given the $10,000 limitation on state and local tax deductions for individuals, assess the advantages of participating in the Pass-Through Entity (PTE) tax regime. Many states allow pass-through entities to pay and deduct the full state taxes on behalf of partners/shareholders. If you receive substantial income from a partnership or S corporation, consider engaging in the PTE tax regime when recommended by the entity representative. Alternatively, if you hold a significant stake in a pass-through entity not currently electing this option, it’s worthwhile to explore whether participating makes sense for your overall tax strategy.
Strengthen your financial foundation and simultaneously impact your tax liabilities by directing funds into your 401(k) or IRA. Capitalize on valuable tax advantages, including tax-deferred growth and potential deductions. For the tax year 2023, individuals can contribute up to $22,500 to their 401(k), with an additional $7,500 catch-up contribution for those aged 50 or older. Traditional IRA contributions are capped at $6,500, with a $1,000 catch-up provision for individuals over 50. Remember to make contributions by April 15, 2024, to qualify for the 2023 tax year. This proactive approach allows you to fortify your financial future while making a meaningful impact on your tax obligations.
Taking a proactive approach to tax planning can yield significant benefits for your next tax bill. Strategically assessing your financial landscape and implementing these practical tips can help you navigate the complexities of the 2023 tax year.
Managing federal tax debts exceeding $59,000 requires careful attention and strategic actions. This article discusses the process, implications, and steps to resolve substantial tax debts that could impact your passport status.
A “seriously delinquent” tax debt is a federal tax liability exceeding $59,000 (to increase annually for inflation), including interest and penalties (indexed annually for inflation). It triggers when either a Notice of Federal Tax Lien has been filed, all administrative remedies under IRC §6320 have lapsed, or a levy has been issued.
Upon reaching this threshold, the IRS can report the liability to the U.S. State Department under IRC §7345. The consequence may involve the State Department withholding passport renewals, issuing new passports, or revoking existing ones. U.S. citizens abroad with revoked passports can still use them for return travel to the U.S., as limited passports may be issued.
When the IRS certifies a taxpayer’s debt, they receive Notice CP508C. However, resolution options exist, including:
Several exceptions exist that exclude taxpayers from being considered seriously delinquent, such as bankruptcy, residing in a federally declared disaster area, a debt deemed not collectible due to hardship, or having a pending installment agreement or offer in compromise.
If a taxpayer believes the certification is erroneous or falls into one of the exceptions, they can initiate resolution by contacting the number provided on CP508C. Additionally, taxpayers can file a suit in a Tax Court or district court to challenge the accuracy of the certification.
Upon successfully resolving the tax issue, the IRS commits to reversing the certification within 30 days, allowing individuals to regain control over their passport status.
Stay informed and proactively address substantial tax debts and passport-related concerns. Understanding the process and available options is crucial for business owners navigating the complexities of IRS certification. If you are in this situation, take the necessary steps to resolve the issue and regain control over your financial and travel matters.
Life insurance can provide peace of mind, but if your estate will be large enough that estate taxes will be a concern, it’s important to not own the policy at death. The policy’s proceeds will be included in your taxable estate and may be subject to estate tax. To avoid this result, a common estate planning strategy is to draft an irrevocable life insurance trust (ILIT) to hold the policy.
Generally, the proceeds of a life insurance policy aren’t included in your taxable estate if you don’t own the policy. However, life insurance proceeds will be included if you possess any “incidents of ownership” over the policy. This goes beyond mere ownership. If you have the right to amend the policy — say, by changing the beneficiaries — or you can borrow against the cash value, it’s treated as an incident of ownership.
Avoiding incidents of ownership can be important because the top estate tax rate is currently 40%. Fortunately, with your gift and estate tax exemption, you can shelter up to $12.92 million (for 2023) of assets from federal gift and estate tax. But be aware that, without congressional action, after 2025 the exemption is scheduled to revert to $5 million (indexed for inflation).
Furthermore, you may have to contend with estate or inheritance tax at the state level. In any event, the estate tax treatment of life insurance policies is a prime consideration in estate planning, especially for wealthier individuals.
A common method for avoiding these estate tax complications is to use an ILIT. This may be accomplished by setting up a trust as the owner of the life insurance policy when the coverage is purchased or by transferring an existing policy to the trust.
The trust must be “irrevocable,” as the name states. In other words, you must relinquish any control over the ILIT, such as the right to revise beneficiaries or revoke the trust. Similarly, acting as the trustee of the ILIT will be treated as an incident of ownership that invalidates the trust.
You’ll designate the ILIT as the primary beneficiary of the life insurance policy. On your death, the proceeds are deposited into the ILIT and held for distribution to the trust’s beneficiaries, such as your spouse, children, grandchildren or other family members.
Naming your surviving spouse as the sole beneficiary can be problematic, however. It may merely delay estate tax liability until your spouse dies.
There are several pitfalls to watch for when transferring an insurance policy to an ILIT. Significantly, if you transfer an existing policy to the ILIT and die within three years of the transfer, the proceeds will be included in your taxable estate. One way to avoid this is to have the ILIT purchase the policy on your life and then fund the trust with enough money over time to pay the premiums.
Also bear in mind that the transfer of an existing policy to an ILIT is considered a taxable gift. Further, subsequent transfers to the trust would also be treated as gifts. The gifts can be sheltered from tax by your available gift and estate tax exemption.
Life insurance is a powerful estate planning tool. It creates an instant source of wealth and liquidity to meet your family’s financial needs after you’re gone. To shield proceeds from estate tax, consider creating an ILIT to hold your policy. Contact your estate planning advisor to determine if an ILIT is right for your estate plan.
© 2023
In today’s competitive business landscape, understanding the intricate world of tax regulations is more than just compliance – it’s a strategic imperative for maximizing profitability. Effective tax planning is a vital component of financial management for business owners, influencing key decisions and shaping the path to growth and success.
Tax planning is not just an annual ritual; it’s an ongoing process that requires foresight and strategic thinking. It involves understanding how different tax regulations impact your business operations and making informed decisions to minimize liabilities and maximize returns.
Strategic decision-making can be impacted by tax planning. Many crucial business choices, from investment options and capital allocation to expansion strategies, may offer opportunities for advanced tax planning. This involves identifying tax-efficient strategies to maximize deductions, credits, and incentives, especially beneficial in sectors like renewable energy or technology.
The choice of business structure –sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation – carries significant tax implications. Understanding how each structure affects your tax obligations can guide you in structuring or restructuring your business for optimal tax efficiency.
Tax rates and regulations can vary significantly across regions. This aspect is crucial for businesses considering expansion or relocation. Analyzing local tax environments can lead to more informed geographical decisions, balancing operational costs with tax advantages.
Tax planning plays a critical role in managing both capital and operational costs. It involves strategies like timing expenses, purchases, and other financial moves to align with favorable tax conditions.
Staying abreast of potential tax laws and policy changes is crucial for proactive planning. This foresight allows businesses to adjust strategies in advance, avoiding surprises and capitalizing on new opportunities.
Effective tax management is crucial for maximizing profitability and ensuring long-term business success. Here are 4 tax management techniques you can put into practice today.
Regularly review your expenses to identify all possible deductions. Keep abreast of new tax credits your business might qualify for, especially those related to innovation or environmental sustainability.
Explore opportunities to defer taxes, such as pension plans or other retirement savings options, which can significantly reduce current tax liabilities.
Implementing tax management software can help track expenses, manage deductions, and stay compliant with ever-changing tax laws.
Consulting with tax professionals can provide insights into complex tax scenarios and assist in strategic planning tailored to your business needs.
By understanding and utilizing tax planning as a strategic tool, you empower your business not just to comply with tax laws but to leverage them as a lever for financial success and stability.
Tax credits are far more valuable than tax deductions. Unlike a deduction, which reduces a business’s taxable income, a credit reduces the business’s tax liability dollar for dollar. Tax credits aren’t unlimited, however. For businesses, the aggregate value of tax credits may be limited by the general business credit (GBC), found in Internal Revenue Code Section 38. Taxpayers should familiarize themselves with the GBC so they can understand the value of their business credits and identify tax-saving opportunities.
The GBC isn’t a tax credit in the usual sense. Rather, it’s a collection of dozens of business-related credits scattered throughout the tax code. (See the sidebar, “What’s included in the GBC?”) Each credit must be claimed separately, according to its specific rules and using the relevant tax forms. Taxpayers that claim more than one credit, however, must also file Form 3800 to report the aggregate value of those credits and calculate the overall allowable credit under the GBC.
The GBC limits total credits in a given year to the excess (if any) of a taxpayer’s net income tax over the greater of:
For purposes of calculating the GBC, “net income tax” is the sum of the taxpayer’s regular tax liability and AMT liability, reduced by certain non-GBC credits. “Net regular tax liability” is regular tax liability reduced by certain credits.
The GBC limit essentially prevents taxpayers from using credits to avoid AMT. In recent years, that hasn’t been an issue for C corporations, because the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) repealed the corporate AMT. Although the recently enacted Inflation Reduction Act established a new corporate minimum tax for corporations with “book profits” over $1 billion for tax years beginning after December 31, 2022, it generally doesn’t limit the GBC.
The AMT for individuals still exists, though the TCJA substantially increased the AMT exemption and made other changes that mean fewer taxpayers are subject to it. Nevertheless, AMT still may limit the use of the GBC by individual taxpayers such as sole proprietors, partners and S corporation shareholders.
If the limits prevent a taxpayer from using all of the GBC, the unused credit may be carried back one year and then, if unused credit remains, carried forward up to 20 years. In a given year, the GBC is used in the following order:
These ordering rules essentially apply a first-in, first-out (FIFO) approach that minimizes the risk that unused credits will expire. Still, taxpayers with a large surplus of credits may risk losing credits that can’t be used within the 20-year carryforward period. Fortunately, the tax code provides some relief for taxpayers in this position.
To prevent taxpayers from “double-dipping,” the tax code generally doesn’t permit them to claim a tax credit and a tax deduction based on the same expenses. Thus, in the year that a GBC is generated, taxpayers generally must treat a portion of its expenses (equal to the amount of the credit) as nondeductible.
In many cases, when a credit is lost, Section 196 allows the lost credit amount to be claimed as a deduction. If the credit is lost because the 20-year carryforward period expires, the taxpayer may claim the deduction in the following tax year. If it’s lost because the taxpayer dies or ceases to exist, the deduction may be claimed for the year of death or cessation.
The Sec. 196 deduction may provide a tax-saving opportunity for C corporations contemplating a sale. It’s common for buyers to acquire a company’s stock and then make an election to treat the transaction as a deemed asset sale for tax purposes. But this can trigger substantial taxable gains for the seller. If the seller has significant unused GBCs, it may be able to use a Sec. 196 deduction to offset some or all of those gains (because the selling corporation ceases to exist).
Determining GBCs for a given year, and calculating applicable limits, can be complicated. Be sure to work with your tax advisor to make the most of these valuable credits.
A general business credit (GBC) consists of more than 30 individual tax credits that provide incentives for a variety of business activities. Examples include:
© 2023
The holiday season is here. During this festive season, your business may want to show its gratitude to employees and customers by giving them gifts or hosting holiday parties. It’s a good time to review the tax rules associated with these expenses. Are they tax deductible by your business and is the value taxable to the recipients?
Many businesses want to show their employees appreciation during the holiday time. In general, anything of value that you transfer to an employee is included in his or her taxable income (and, therefore, subject to income and payroll taxes) and deductible by your business.
But there’s an exception for noncash gifts that constitute a “de minimis” fringe benefit. These are items small in value and given so infrequently that they are administratively impracticable to account for. Common examples include holiday turkeys or hams, gift baskets, occasional sports or theater tickets (but not season tickets), and other low-cost merchandise.
De minimis fringe benefits aren’t included in your employees’ taxable income yet they’re still deductible by your business. Unlike gifts to customers, there’s no specific dollar threshold for de minimis gifts. However, many businesses use an informal cutoff of $75.
Key point: Cash gifts — as well as cash equivalents, such as gift cards — are included in an employee’s income and subject to payroll tax withholding regardless of how small they are and infrequently they’re given.
If you make gifts to customers or clients, they’re only deductible up to $25 per recipient, per year. For purposes of the $25 limit, you don’t need to include “incidental” costs that don’t substantially add to the gift’s value, such as engraving, gift wrapping, packaging or shipping. Also excluded from the $25 limit is branded marketing collateral — such as small items imprinted with your company’s name and logo — provided they’re widely distributed and cost less than $4 each.
The $25 limit is for gifts to individuals. There’s no set limit on gifts to a company (for example, a gift basket for all of a customer’s team members to share) as long as the cost is “reasonable.”
Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, certain deductions for business-related meals were reduced and the deduction for business entertainment was eliminated. However, there’s an exception for certain recreational activities, including holiday parties.
Holiday parties are fully deductible (and excludible from recipients’ income) so long as they’re primarily for the benefit of employees who aren’t highly compensated and their families. If customers, and others also attend, a holiday party may be partially deductible.
Sending holiday cards is a nice way to show customers and clients your appreciation. If you use the cards to promote your business, you can probably deduct the cost. Incorporate your company name and logo, and you might even want to include a discount coupon for your products or services.
If you have questions about giving holiday gifts to employees or customers or throwing a holiday party, contact us. We can explain the tax implications.
© 2023
One of the most appreciated fringe benefits for owners and employees of small businesses is the use of a company car. This perk results in tax deductions for the employer as well as tax breaks for the owners and employees driving the cars. (And of course, they enjoy the nontax benefit of using a company car.) Even better, current federal tax rules make the benefit more valuable than it was in the past.
Let’s take a look at how the rules work in a typical situation. For example, a corporation decides to supply the owner-employee with a company car. The owner-employee needs the car to visit customers and satellite offices, check on suppliers and meet with vendors. He or she expects to drive the car 8,500 miles a year for business and also anticipates using the car for about 7,000 miles of personal driving. This includes commuting, running errands and taking weekend trips. Therefore, the usage of the vehicle will be approximately 55% for business and 45% for personal purposes. Naturally, the owner-employee wants an attractive car that reflects positively on the business, so the corporation buys a new $57,000 luxury sedan.
The cost for personal use of the vehicle is equal to the tax the owner-employee pays on the fringe benefit value of the 45% personal mileage. In contrast, if the owner-employee bought the car to drive the personal miles, he or she would pay out-of-pocket for the entire purchase cost of the car.
Personal use is treated as fringe benefit income. For tax purposes, the corporation treats the car much the same way it would any other business asset, subject to depreciation deduction restrictions if the auto is purchased. Out-of-pocket expenses related to the car (including insurance, gas, oil and maintenance) are deductible, including the portion that relates to personal use. If the corporation finances the car, the interest it pays on the loan is deductible as a business expense (unless the business is subject to the business interest expense deduction limitation under the tax code).
On the other hand, if the owner-employee buys the auto, he or she isn’t entitled to any deductions. Outlays for the business-related portion of driving are unreimbursed employee business expenses, which are nondeductible from 2018 to 2025 due to the suspension of miscellaneous itemized deductions under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. And if the owner-employee finances the car personally, the interest payments are nondeductible.
One other implication: The purchase of the car by the corporation has no effect on the owner-employee’s credit rating.
Supplying a vehicle for an owner’s or key employee’s business and personal use comes with complications and paperwork. Personal use needs to be tracked and valued under the fringe benefit tax rules and treated as income. This article only explains the basics.
Despite the necessary valuation and paperwork, a company-provided car is still a valuable fringe benefit for business owners and key employees. It can provide them with the use of a vehicle at a low tax cost while generating tax deductions for their businesses. (You may even be able to transfer the vehicle to the employee when you’re ready to dispose of it, but that involves other tax implications.) We can help you stay in compliance with the rules and explain more about this fringe benefit.
© 2023
Every business owner should have an exit strategy that helps recoup the maximum amount for his or her investment. Understanding the tax implications of a business sale will help you plan for — and, in some cases, reduce — the tax impact. One option is to sell your business to a third party. Here are some considerations to help ensure the transition is as smooth as possible.
Start by obtaining a professional valuation of your business to give you an idea of what the business is currently worth. The valuation process also will help you understand what factors drive the value of your business and identify any weaknesses that reduce its value.
Once you’ve received a valuation, you can make changes to enhance the business’s value and potentially increase the selling price. For example, if the valuator finds that the business relies too heavily on your management skills, bringing in new management talent may make the business more valuable to a prospective buyer.
A valuation can also reveal concentration risks. For instance, if a significant portion of your business is concentrated in a handful of customers or one geographical area, you could take steps to diversify your customer base.
Corporate sellers generally prefer selling stock rather than assets. That’s because the profit on a stock sale is generally taxable at more favorable long-term capital gains rates, while asset sales generate a combination of capital gains and ordinary income. For a business with large amounts of depreciated machinery and equipment, asset sales can generate significant ordinary income in the form of depreciation recapture. (Note: The tax rate on recaptured depreciation of certain real estate is capped at 25%.)
In addition, if your company is a C corporation, an asset sale can trigger double taxation: once at the corporate level and a second time when the proceeds are distributed to shareholders as a dividend. In a stock sale, the buyer acquires the stock directly from the shareholders, so there’s no corporate-level tax.
Buyers, on the other hand, almost always prefer to buy assets, especially for equipment-intensive businesses, such as manufacturers. Acquiring assets provides the buyer with a fresh tax basis in the assets for depreciation purposes and allows the buyer to avoid assuming the seller’s liabilities.
Given the significant advantages of buying assets, most buyers are reluctant to purchase stock. But even in an asset sale, there are strategies for a seller to employ to minimize the tax hit. One strategy is to negotiate a favorable allocation of the purchase price. Although tax rules require the purchase price allocation to be reasonable in light of the assets’ market values, the IRS will generally respect an allocation agreed on by unrelated parties.
As a seller, you’ll want to allocate as much of the price as possible to assets that generate capital gains, such as goodwill and certain other intangible assets. The buyer will prefer allocations to assets eligible for accelerated depreciation, such as machinery and equipment. However, depreciable assets are likely to generate ordinary income for the seller.
Allocating a portion of the purchase price to goodwill can be a good compromise between the parties’ conflicting interests. Sellers enjoy capital gains treatment while buyers can generally amortize goodwill over 15 years for tax purposes.
If your company is a C corporation, establishing that a portion of goodwill is attributable to personal goodwill — that is, goodwill associated with the reputations of the individual owners rather than the enterprise — can be particularly advantageous. That’s because payments for personal goodwill are made directly to the shareholders, avoiding double taxation.
You may need to take certain steps to transfer personal goodwill to the buyer. This may include executing an employment or consulting agreement that defines your responsibility for ensuring that the buyer enjoys the benefits of your ability to attract and retain customers. Buyers may want a noncompete agreement. These are common in private business sales and can help protect the buyer from competition from the seller after the deal closes.
Different strategies can help you enhance your business’s value and minimize taxes, but they may take some time to put into place. Whatever your exit strategy, the earlier you start planning, the better.
An employee stock ownership plan (ESOP) might be a viable exit strategy if your business is organized as a corporation and you’re not interested in leaving it to your family or selling to an outsider. An ESOP creates a market for your stock, allowing you to cash out of the business and transfer control to the next generation of owners gradually.
An ESOP is a qualified retirement plan that invests in the company’s stock. Benefits to business owners include the ability to:
ESOPs also provide significant tax benefits to the company, including tax deductions for contributions to the ESOP to cover stock purchases and (in the case of a leveraged ESOP) loan payments. S corporations may avoid taxes on income passed through to shares held by the ESOP.
But there are some downsides, too. For example, ESOPs are subject to many of the same rules and restrictions as 401(k) and other employer-sponsored plans. And they can involve significant administrative costs, including annual appraisals of the company’s stock. Contact your tax advisor to discuss if an ESOP is right for your business.
© 2023
Gaining a competitive edge in today’s market requires more than understanding one’s financials. It requires using financial metrics strategically to enhance business success. The Profit Margin Ratio is a crucial financial metric that predicts future viability and competitiveness.
Profit margins allow businesses to identify operational efficiencies or deficiencies. It’s not about the total dollars earned. This ratio reveals what percentage of sales remains after covering the costs, providing a clear view of profitability.
Profit Margin Ratios come in 3 types: Gross, Operating, and Net. Each offers unique insights:
For example, with $1 million in revenue, a company’s Gross Profit Margin at a direct cost of $600,000 is 40%. If operating expenses are $200,000, the Operating Margin drops to 20%, and after $100,000 in additional expenses, the Net Profit Margin is 10%.
With these metrics, businesses can pinpoint where to cut costs or where to invest, ensuring sustained growth and profitability.
By monitoring these margins, you can drive improved profitability, effective cost management, and enhanced operational efficiency. They can act as a warning flag to help identify areas to look into when things might not be right. For instance, while a strong Gross Profit Margin alongside a weak Net Profit Margin might show excessive administrative costs; conversely, a weak Gross Profit Margin with a strong Net Profit Margin could signal the need for pricing adjustments to better align with costs, both of which can guide you to specific improvements.
Here are 5 steps you can take to implement profit margin analysis into your business:
Mastering Profit Margin Ratios equips you with the foresight to shape your business’s future. This financial mastery is a map guiding you toward sustainable growth and success. Embrace these insights, and with precision and the right tools, your business is on track to reach its fullest potential.
In the midst of holiday parties and shopping for gifts, don’t forget to consider steps to cut the 2023 tax liability for your business. You still have time to take advantage of a few opportunities.
If your business operates on a cash basis, you can significantly affect your amount of taxable income by accelerating your deductions into 2023 and deferring income into 2024 (assuming you expect to be taxed at the same or a lower rate next year).
For example, you could put recurring expenses normally paid early in the year on your credit card before January 1 — that way, you can claim the deduction for 2023 even though you don’t pay the credit card bill until 2024. In certain circumstances, you also can prepay some expenses, such as rent or insurance and claim them in 2023.
As for deferring income, wait until close to year-end to send out invoices to customers with reliable payment histories. Accrual-basis businesses can take a similar approach, holding off on the delivery of goods and services until next year.
If you’re thinking about purchasing new or used equipment, machinery or office equipment in the new year, it might be time to act now. Buy the assets and place them in service by December 31, and you can deduct 80% of the cost as bonus depreciation in 2023. This is down from 100% for 2022 and it will drop to 60% for assets placed in service in 2024. Contact us for details on the 80% bonus depreciation break and exactly what types of assets qualify.
Bonus depreciation is also available for certain building improvements.
Fortunately, the first-year Section 179 depreciation deduction will allow many small and medium-sized businesses to write off the entire cost of some or all of their 2023 asset additions on this year’s federal income tax return. There may also be state tax benefits.
However, keep in mind there are limitations on the deduction. For tax years beginning in 2023, the maximum Sec. 179 deduction is $1.16 million and a phaseout rule kicks in if you put more than $2.89 million of qualifying assets into service in the year.
The 80% bonus depreciation deduction may have a major tax-saving impact on first-year depreciation deductions for new or used heavy vehicles used over 50% for business. That’s because heavy SUVs, pickups and vans are treated for federal income tax purposes as transportation equipment. In turn, that means they qualify for 100% bonus depreciation.
Specifically, 100% bonus depreciation is available when the SUV, pickup or van has a manufacturer’s gross vehicle weight rating above 6,000 pounds. You can verify a vehicle’s weight by looking at the manufacturer’s label, which is usually found on the inside edge of the driver’s side door. If you’re considering buying an eligible vehicle, placing one in service before year end could deliver a significant write-off on this year’s return.
Keep in mind that some of these tactics could adversely impact other aspects of your tax liability, such as the qualified business income deduction. Contact us to make the most of your tax planning opportunities.
© 2023
If your business completes minor repairs by December 31, you can deduct those costs on your 2023 tax return. But different tax rules apply to improvements. As opposed to repairs, improvements are capital expenditures that must be written off over time.
How can you tell whether work constitutes a repair or an improvement? It can be tricky. Fixing a broken windowpane is clearly a repair, while adding an indoor parking facility is obviously an improvement. But many expenses fall in between those two examples. Fortunately, IRS tangible property regulations offer more clarity.
Notably, the final regulations provide a safe-harbor rule under which you can currently deduct for federal tax purposes amounts paid for tangible property if you deduct those amounts for financial accounting purposes or in keeping your books and records. However, a dollar limit applies:
Additional rules apply that may limit or eliminate your current deduction for a particular expense.
There’s also a small businesses safe harbor under which businesses with $10 million or less in average gross receipts can elect to currently deduct improvements to a building with an unadjusted basis of $1 million or less. However, the total amount paid for repairs, maintenance and improvements to the building can’t exceed the lesser of $10,000 or 2% of the unadjusted basis.
Routine maintenance costs generally are deductible in the year in which they’re incurred. An activity is “routine” if the business reasonably expects to perform it more than once during the property’s useful life (more than once over a 10-year period for buildings). Note: A business may capitalize these costs if this is consistent with its financial statements.
In addition, the traditional rule that improvements are capitalized and depreciated over time remains in place. But the regulations authorize a business to deduct some improvements (for example, an HVAC unit) if they are properly segregated.
If your business makes repairs and improvements at the same time, be aware that the IRS may lump the costs together as a general plan of betterment, causing you to forfeit a current deduction for repairs. All else being equal, arrange repair work separately at another time — preferably before 2024 if you want to reduce your 2023 tax liability.
© 2023
The IRS recently announced various inflation-adjusted federal income tax amounts. Here’s a rundown of the amounts that are most likely to affect small businesses and their owners.
If you run your business as a sole proprietorship or pass-through business entity (LLC, partnership or S corporation), the business’s net ordinary income from operations is passed through to you and reported on your personal Form 1040. You then pay the individual federal income tax rates on that income.
Here are the 2024 inflation adjusted bracket thresholds.
Key Point: These thresholds are about 5.4% higher than for 2023. That means that, other things being equal, you can have about 5.4% more ordinary business income next year without owing more to Uncle Sam.
If you run your business as a sole proprietorship or a pass-through entity, and the business sells assets, you may have Section 1231 gains that passed through to you to be included on your personal Form 1040. Sec. 1231 gains are long-term gains from selling business assets that were held for more than one year, and they’re generally taxed at the same lower federal rates that apply to garden-variety long-term capital gains (LTCGs), such as stock sale gains. Here are the 2024 inflation-adjusted bracket thresholds that will generally apply to Sec. 1231 gains recognized by individual taxpayers.
If you run your business as a C corporation, and the company pays you qualified dividends, they’re taxed at the lower LTCG rates. So, the 2024 rate brackets for qualified dividends paid to individual taxpayers will be the same as above.
If you operate your business as a sole proprietorship or as a pass-through entity, you probably have net self-employment (SE) income that must be reported on your personal Form 1040 to calculate your SE tax liability. For 2024, the maximum 15.3% SE tax rate will apply to the first $166,800 of net SE income (up from $160,200 for 2023).
For tax years beginning in 2024, small businesses can potentially write off up to $1,220,000 of qualified asset additions in year one (up from $1,160,000 for 2023). However, the maximum deduction amount begins to be phased out once qualified asset additions exceed $3,050,000 (up from $2,890,000 for 2023). Various limitations apply to Sec. 179 deductions.
Side Note: Under the first-year bonus depreciation break, you can deduct up to 60% of the cost of qualified asset additions placed in service in calendar year 2024. For 2023, you could deduct up to 80%.
These are only the 2024 inflation-adjusted amounts that are most likely to affect small businesses and their owners. There are others that may potentially apply, including: limits on qualified business income deductions and business loss deductions, income limits on various favorable exceptions such as the right to use cash-method accounting, limits on how much you can contribute to your self-employed or company-sponsored tax-favored retirement account, limits on tax-free transportation allowances for employees, and limits on tax-free adoption assistance for employees. Contact us with questions about your situation.
© 2023
The imminent enforcement of the Corporate Transparency Act (CTA) is a critical turning point that demands immediate attention from business owners to avoid severe penalties. Ultimately, business owners need to understand that it’s the business owner’s responsibility to ensure you are following and meeting all reporting requirements for your business. This article will review some key points within the CTA, and business owners are advised to review the CTA to understand all of its requirements as they pertain to their specific situation.
Under the CTA, the Beneficial Ownership Reporting requirements will be effective January 1, 2024. This reporting requirement mandates most U.S. corporate entities and foreign entities operating in the U.S. to report ownership information to the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). The CTA’s enactment establishes unprecedented protocols, compelling reporting entities to disclose the identities of their beneficial owners.
Key terms and definitions to know from the CTA:
All reporting companies will submit their information electronically through the Beneficial Ownership Secure System (BOSS). The system is still in development and has not been launched as of the date of this article. You can expect detailed guidelines from FinCEN that will direct your next steps once it has.
Reporting requirements do not start until January 1, 2024, and FinCEN will not accept any reports until then. However, preparing your business for this reporting requirement is essential. The enforcement of the CTA includes significant penalties, including daily fines and possible imprisonment for non-compliance.
Key timeframes:
The CTA is not just a regulatory hurdle; it’s a chance to build trust with clients and partners by demonstrating your commitment to transparency and ethical business practices. By embracing these changes, you comply with the law and position your business as trustworthy in a competitive market. While the requirements can seem daunting on the surface, reach out to our firm, and we can help you navigate and guide your research.
Additional resources for information: Small Entity Compliance Guide
If you have a parent entering a nursing home, taxes are probably the last thing on your mind. But you should know that several tax breaks may be available to help offset some of the costs.
The costs of qualified long-term care (LTC), such as nursing home care, may be deductible as medical expenses to the extent they, along with other qualified expenses, exceed 7.5% of adjusted gross income (AGI). But keep in mind that the medical expense deduction is an itemized deduction. And itemizing deductions saves taxes only if total itemized deductions exceed the applicable standard deduction.
Amounts paid to a nursing home are deductible as medical expenses if a person is staying at the facility principally for medical, rather than custodial care. Also, for those individuals, only the portion of the fee that’s allocable to actual medical care qualifies as a deductible expense.
If the individual is chronically ill, all qualified LTC services are deductible. Qualified LTC services are those required by a chronically ill individual and administered by a licensed health care practitioner. They include diagnostic, preventive, therapeutic, curing, treating, mitigating and rehabilitative services, and maintenance or personal-care services.
For someone to qualify as chronically ill, a physician or other licensed health care practitioner must certify him or her as unable to perform at least two activities of daily living (ADLs) for at least 90 days due to a loss of functional capacity or severe cognitive impairment. ADLs include eating, transferring, bathing, dressing, toileting and continence.
If your parent qualifies as your dependent, you can add medical expenses you incur for him or her to your own medical expenses when calculating your medical expense deduction. We can help with this determination.
If you aren’t married and you meet the dependency tests for your parent, you may qualify for head-of-household filing status, which has a higher standard deduction and lower tax rates than filing as single. You may be eligible to use this status even if the parent for whom you claim an exemption doesn’t live with you.
In many cases, a move to a nursing home also means selling the parent’s home. Fortunately, up to $250,000 of gain from the sale of a principal residence may be tax-free. To qualify for the $250,000 exclusion, the seller must generally have owned the home for at least two years of the five years before the sale.
Also, the seller must have used the home as a principal residence for at least two of the five years before the sale. However, there’s an exception to the two-of-five-year use test for a seller who becomes physically or mentally unable to care for him- or herself during the five-year period.
Perhaps your parent is still in good health but is paying for LTC insurance (or you’re paying LTC insurance premiums for yourself). If so, be aware that premiums paid for a qualified LTC insurance contract are deductible as medical expenses (subject to limits) to the extent that they, when combined with other medical expenses, exceed the 7.5%-of-AGI threshold. Such a contract doesn’t provide payment for costs covered by Medicare, is guaranteed renewable and doesn’t have a cash surrender value.
The amount of qualified LTC premiums that can be included as medical expenses is based on the age of the insured individual. For example, for 2023 the limit on deductible premiums is $4,770 for those 61 to 70 years old and $5,960 for those over 70.
This is just a brief overview of tax breaks that may help offset nursing home and related costs. Contact us if you need more information or assistance.
© 2023
Is your business depreciating over 30 years the entire cost of constructing the building that houses your enterprise? If so, you should consider a cost segregation study. It may allow you to accelerate depreciation deductions on certain items, thereby reducing taxes and boosting cash flow.
Business buildings generally have a 39-year depreciation period (27.5 years for residential rental properties). In most cases, a business depreciates a building’s structural components, including walls, windows, HVAC systems, elevators, plumbing and wiring, along with the building. Personal property — including equipment, machinery, furniture and fixtures — is eligible for accelerated depreciation, usually over five or seven years. And land improvements, such as fences, outdoor lighting and parking lots, are depreciable over 15 years.
Frequently, businesses allocate all or most of their buildings’ acquisition or construction costs to real property, overlooking opportunities to allocate costs to shorter-lived personal property or land improvements. In some cases, the distinction between real and personal property is obvious. For example, computers and furniture are personal property. But the line between real and personal property is not always clear. Items that appear to be “part of a building” may in fact be personal property. Examples are removable wall and floor coverings, removable partitions, awnings and canopies, window treatments, decorative lighting and signs.
In addition, certain items that otherwise would be treated as real property may qualify as personal property if they serve more of a business function than a structural purpose. These include reinforced flooring that supports heavy manufacturing equipment, electrical or plumbing installations required to operate specialized equipment and dedicated cooling systems for data processing rooms.
A cost segregation study combines accounting and engineering techniques to identify building costs that are properly allocable to tangible personal property rather than real property. Although the relative costs and benefits of a cost segregation study depend on your particular facts and circumstances, it can be a valuable investment.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) enhanced certain depreciation-related tax breaks, which may also enhance the benefits of a cost segregation study. Among other changes, the law permanently increased limits on Section 179 expensing, which allows you to immediately deduct the entire cost of qualifying equipment or other fixed assets up to specified thresholds.
In addition, the TCJA expanded 15-year-property treatment to apply to qualified improvement property. Previously, this tax break was limited to qualified leasehold-improvement, retail-improvement and restaurant property. And the law temporarily increased first-year bonus depreciation from 50% to 100% in 2022, 80% in 2023 and 60% in 2024. After that, it will continue to decrease until it is 0% in 2027, unless Congress acts.
It isn’t too late to get the benefit of faster depreciation for items that were incorrectly assumed to be part of your building for depreciation purposes. You don’t have to amend your past returns (or meet a deadline for claiming tax refunds) to claim the depreciation that you could have already claimed. Instead, you can claim that depreciation by following procedures, in connection with the next tax return you file, that will result in automatic IRS consent to a change in your accounting for depreciation.
Cost segregation studies can yield substantial benefits, but they’re not the best move for every business. Contact us to determine whether this strategy would work for your business. We’ll judge whether a study will result in tax savings that are greater than the costs of the study itself.
© 2023
If leaving a charitable legacy is important to you, you may be thinking about establishing a private foundation or other vehicle for managing your philanthropic activities. Private foundations can be highly effective, but they’re expensive to set up and operate. Donor-advised funds (DAFs) are popular alternatives, but they also have potential drawbacks.
Why use a foundation or DAF? Can’t you just write checks to your charities of choice? Of course, but contributing funds to a private foundation or DAF allows you to enjoy immediate charitable tax deductions without needing to identify specific beneficiaries or make contributions right away. It gives you more time to research potential recipients or change the organizations you support from year to year.
These vehicles also allow you to involve your family in your charitable endeavors. You can name family members to the board of a private foundation or even hire loved ones to manage it. Many DAFs allow you to designate a successor advisor.
A private foundation is a charitable organization, typically structured as a trust or corporation and designed to accept donations from a small group of people, such as you and your family. Private foundations usually make grants to other charitable organizations rather than provide charitable services themselves.
A DAF is an investment account, controlled by a sponsoring organization — usually, a public charity or community foundation — and often managed by an investment firm. The fund accepts tax-deductible contributions from investors, who advise the fund on how their charitable dollars should be spent.
DAFs generally can be set up in a matter of days — or even hours. Setting up a private foundation, however, takes time, since it involves establishing a legal entity. Another advantage of DAFs is that they’re inexpensive (or free) to create, and minimum initial contributions can be as low as $5,000. In contrast, starting a private foundation involves significant legal and accounting fees. Foundations also require much larger initial contributions — typically hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars — to justify their start-up and ongoing administrative expenses.
Here are other ways the two vehicles compare:
Operating expenses. DAFs typically charge management and investment fees of around 1% to 2% of your account balance. Managing a private foundation is much more expensive since you’ll need to appoint a board, hold periodic meetings, keep minutes, file separate tax returns, and incur ongoing legal and accounting costs, in addition to paying investment fees. You’ll also need to hire a staff or engage a third-party administrator, and pay an excise tax on net investment income (currently 1.39%).
Distribution requirements. DAFs aren’t subject to required minimum distributions, so investments can grow tax-free indefinitely (subject to any rules of the sponsoring organization). But private foundations must distribute at least 5% of their net market value each year.
Charitable recipients. Distributions from DAFs must be made to public charities. Private foundations can make grants to a wider range of charitable recipients, including individuals (subject to certain restrictions).
Tax deductibility. Cash contributions to DAFs are tax deductible up to 50% of the donor’s adjusted gross income (AGI), while noncash contributions are generally deductible up to 30% of AGI. For private foundations, the deduction limits are 30% and 20%, respectively. Typically, you can deduct the market value of appreciated assets donated to a DAF. Deductions for donations to foundations are limited to your cost basis (except for publicly traded stock).
Privacy. DAFs are permitted to accept donations privately, so it’s possible for contributors to remain anonymous. Private foundations must publicly disclose the names of donors who give more than $5,000.
Control. This is an area where private foundations have a clear advantage. You and other board members retain full control over the foundation’s investments and distributions. DAF contributions become the sponsor’s property and your role in managing investments and distributions is strictly advisory. Practically speaking, however, sponsors almost always follow contributors’ advice.
The right charitable giving vehicle for you depends on many factors, including your financial resources, the charities you wish to support and the level of control you desire. Talk to your advisors about designing a philanthropic strategy that meets your needs.
© 2023
If you’re planning to start a business or thinking about changing your business entity, you need to determine what will work best for you. Should you operate as a C corporation or a pass-through entity such as a sole-proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC) or S corporation? There are many issues to consider.
Currently, the corporate federal income tax is imposed at a flat 21% rate, while individual federal income tax rates currently begin at 10% and go up to 37%. The difference in rates can be alleviated by the qualified business income (QBI) deduction that’s available to eligible pass-through entity owners that are individuals, and some estates and trusts.
Individual rate caveats: The QBI deduction is scheduled to end in 2026, unless Congress acts to extend it, while the 21% corporate rate is not scheduled to expire. Also, noncorporate taxpayers with modified adjusted gross incomes above certain levels are subject to an additional 3.8% tax on net investment income.
Organizing a business as a C corporation instead of a pass-through entity may reduce the current federal income tax on the business’s income. The corporation can still pay reasonable compensation to the shareholders and pay interest on loans from the shareholders. That income will be taxed at higher individual rates, but the overall rate on the corporation’s income can be lower than if the business was operated as a pass-through entity.
There are other tax-related factors to take into consideration. For example:
As you can see, there are many factors involved in operating a business as a certain type of entity. This only covers a few of them. For more details about how to proceed in your situation, consult with us.
© 2023
In the business world, blending passion with profitability is essential. Financial accounting has evolved into a strategic cornerstone that sets successful enterprises apart. In the age of data-driven decision-making, integrating financial strategy is vital. This article will help you understand how strong financial accounting can help you achieve your goals.
Once regarded as a mere reporting tool, financial accounting now plays a crucial strategic role in advancing your business’s growth. This shift is driven by the concept that every financial data point conveys essential narratives about market trends, operational efficiencies, and untapped growth prospects. Understanding these insights can help you make better decisions that fuel your growth.
When it comes to making finance more strategic, consider starting with the metrics you are reviewing. The right metrics will not only help you manage and make more informed decisions about your business.
By integrating these financial metrics into your regular analysis, you can understand where your business stands financially and what strategic moves you can make to enhance its financial performance and value creation.
Outside of upgrading the metrics you monitor, it’s also important to build a scorecard for your business. Beyond enhancing the metrics you track, it’s also vital to construct a business scorecard. The Balanced Scorecard approach goes beyond conventional financial measures, providing a holistic perspective of your organization that’s essential for long-term growth. This strategic planning and management system empowers you to align your business activities with the company’s vision and strategy, enhance both internal and external communication, and continually assess organizational performance relative to strategic objectives. Four Key areas to consider for your scorecard are listed below.
By integrating these four perspectives, the Balanced Scorecard helps you not only measure current performance but also provides a roadmap for operational excellence that drives future financial success.
The future belongs to businesses that blend financial acumen with operational prowess. Pause for a moment. Is your business truly leveraging the potential of integrated financial accounting? Reflect, re-strategize, and re-align. Need help? Reach out to see how we can help you make finance more strategic.
You may be familiar with the rule that permits a business to deduct employee bonuses this year if it pays them within 2½ months after the end of the tax year. It’s an attractive year-end planning technique that benefits your business and your employees: You enjoy a tax deduction this year, while your employees needn’t report the income until next year.
These tax benefits aren’t always available, however, so it’s important to understand the requirements. Here’s a quick review.
If your business uses the cash method of accounting, you must deduct bonuses in the year they’re paid, even if they’re earned in the previous year. To accelerate bonus deductions into this year, your business must be on the accrual method of accounting.
Favorable tax treatment is limited to bonuses paid to unrelated parties. For a corporation, a related party is an individual who owns more than 50% of the company. For S corporations, partnerships and limited liability companies, related parties include any of their shareholders, partners or members.
Even if the first two requirements are met, you can’t deduct a bonus this year unless it’s fixed and determinable as of December 31. Generally, this means that:
Many companies get tripped up by the “fixed and determinable” requirement because their bonus plans condition payment on the recipient’s continued employment through the payment date. If employees who leave the company before the payment date forfeit their bonuses, the company’s liability isn’t established by year end.
There may be a way to avoid this problem, however. Under IRS guidance, it’s possible to deduct bonuses earned this year, even if there’s a risk of forfeiture. The solution can be to use a properly designed bonus pool. For this strategy to work, the aggregate amount in the pool must be fixed by the end of the year. And, any forfeited bonuses must be reallocated among the remaining employees.
If you wish to accelerate deductions for bonuses paid next year, consult your CPA to make sure that you meet the requirements. It’s critical to design your bonus plan carefully to avoid any language that suggests bonuses aren’t fixed by the end of the year, such as retaining discretion to modify or cancel them or conditioning payment on board approval.
© 2023
Are employees at your business traveling and frustrated about documenting expenses? Or perhaps you’re annoyed at the time and energy that goes into reviewing business travel expenses. There may be a way to simplify the reimbursement of these expenses. In Notice 2023-68, the IRS announced the fiscal 2024 special “per diem” rates that became effective October 1, 2023. Taxpayers can use these rates to substantiate the amount of expenses for lodging, meals and incidentals when traveling away from home. (Taxpayers in the transportation industry can use a special transportation industry rate.)
A simplified alternative to tracking actual business travel expenses is to use the “high-low” per diem method. This method provides fixed travel per diems. The amounts, provided by the IRS, vary from locality to locality.
Under the high-low method, the IRS establishes an annual flat rate for certain areas with higher costs of living. All locations within the continental United States that aren’t listed as “high-cost” are automatically considered “low-cost.” The high-low method may be used in lieu of the specific per diem rates for business destinations. Examples of high-cost areas include Boston, and San Francisco. Other locations, such as resort areas, are considered high-cost during only part of the year.
Under some circumstances — for example, if an employer provides lodging or pays the hotel directly — employees may receive a per diem reimbursement only for their meals and incidental expenses. There’s also a $5 incidental-expenses-only rate for employees who don’t pay or incur meal expenses for a calendar day (or partial day) of travel.
If your company uses per diem rates, employees don’t have to meet the usual recordkeeping rules required by the IRS. Receipts of expenses generally aren’t required under the per diem method. But employees still must substantiate the time, place and business purpose of the travel. Per diem reimbursements generally aren’t subject to income or payroll tax withholding or reported on an employee’s Form W-2.
For travel after September 30, 2023, the per diem rate for all high-cost areas within the continental United States is $309. This consists of $235 for lodging and $74 for meals and incidental expenses. For all other areas within the continental United States, the per diem rate is $214 for travel after September 30, 2023 ($150 for lodging and $64 for meals and incidental expenses). Compared to the FY2023 per diems, the high-cost area per diem increased $12, and the low-cost area per diem increased $10.
Important: This method is subject to various rules and restrictions. For example, companies that use the high-low method for an employee must continue using it for all reimbursement of business travel expenses within the continental United States during the calendar year. However, the company may use any permissible method to reimburse that employee for any travel outside the continental United States.
For travel during the last three months of a calendar year, employers must continue to use the same method (per diem or high-low method) for an employee as they used during the first nine months of the calendar year. Also, note that per diem rates can’t be paid to individuals who own 10% or more of the business.
If your employees are traveling, it may be a good time to review the rates and consider switching to the high-low method. It can reduce the time and frustration associated with traditional travel reimbursement. Contact us for more information or read the IRS notice here.
© 2023
The Social Security Administration recently announced that the wage base for computing Social Security tax will increase to $168,600 for 2024 (up from $160,200 for 2023). Wages and self-employment income above this threshold aren’t subject to Social Security tax.
The Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) imposes two taxes on employers, employees and self-employed workers — one for Old Age, Survivors and Disability Insurance, which is commonly known as the Social Security tax, and the other for Hospital Insurance, which is commonly known as the Medicare tax.
There’s a maximum amount of compensation subject to the Social Security tax, but no maximum for Medicare tax. For 2024, the FICA tax rate for employers will be 7.65% — 6.2% for Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare (the same as in 2023).
For 2024, an employee will pay:
For 2024, the self-employment tax imposed on self-employed people will be:
You may have questions if an employee who works for your business has a second job. That employee would have taxes withheld from two different employers. Can the employee ask you to stop withholding Social Security tax once he or she reaches the wage base threshold? The answer is no. Each employer must withhold Social Security taxes from the individual’s wages, even if the combined withholding exceeds the maximum amount that can be imposed for the year. Fortunately, the employee will get a credit on his or her tax return for any excess withheld.
Do you have questions about payroll tax filing or payments? Contact us. We’ll help ensure you stay in compliance.
© 2023
Do you use an automobile in your trade or business? If so, you may question how depreciation tax deductions are determined. The rules are complicated, and special limitations that apply to vehicles classified as passenger autos (which include many pickups and SUVs) can result in it taking longer than expected to fully depreciate a vehicle.
First, be aware that separate depreciation calculations for a passenger auto only come into play if you choose to use the actual expense method to calculate deductions. If, instead, you use the standard mileage rate (65.5 cents per business mile driven for 2023), a depreciation allowance is built into the rate.
If you use the actual expense method to determine your allowable deductions for a passenger auto, you must make a separate depreciation calculation for each year until the vehicle is fully depreciated. According to the general rule, you calculate depreciation over a six-year span as follows: Year 1, 20% of the cost; Year 2, 32%; Year 3, 19.2%; Years 4 and 5, 11.52%; and Year 6, 5.76%. If a vehicle is used 50% or less for business purposes, you must use the straight-line method to calculate depreciation deductions instead of the percentages listed above.
For a passenger auto that costs more than the applicable amount for the year the vehicle is placed in service, you’re limited to specified annual depreciation ceilings. These are indexed for inflation and may change annually. For example, for a passenger auto placed in service in 2023 that cost more than a certain amount, the Year 1 depreciation ceiling is $20,200 if you choose to deduct first-year bonus depreciation. The annual ceilings for later years are: Year 2, $19,500; Year 3, $11,700; and for all later years, $6,960 until the vehicle is fully depreciated.
These ceilings are proportionately reduced for any nonbusiness use. And if a vehicle is used 50% or less for business purposes, you must use the straight-line method to calculate depreciation deductions.
Reminder: Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, bonus depreciation is being phased down to zero in 2027, unless Congress acts to extend it. For 2023, the deduction is 80% of eligible property and for 2024, it’s scheduled to go down to 60%.
Much more favorable depreciation rules apply to heavy SUVs, pickups, and vans used over 50% for business, because they’re treated as transportation equipment for depreciation purposes. This means a vehicle with a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) above 6,000 pounds. Quite a few SUVs and pickups pass this test. You can usually find the GVWR on a label on the inside edge of the driver-side door.
What’s the impact of these depreciation limits on your business vehicle decisions? They change the after-tax cost of passenger autos used for business. That is, the true cost of a business asset is reduced by the tax savings from related depreciation deductions. To the extent depreciation deductions are reduced, and thereby deferred to future years, the value of the related tax savings is also reduced due to time-value-of-money considerations, and the true cost of the asset is therefore that much higher.
The rules are different if you lease an expensive passenger auto used for business. Contact us if you have questions or want more information.
© 2023
Ever wonder how IRS examiners know about different industries so they can audit various businesses? They generally do research about specific industries and issues on tax returns by using IRS Audit Techniques Guides (ATGs). A little-known fact is that these guides are available to the public on the IRS website. In other words, your business can use the same guides to gain insight into what the IRS is looking for in terms of compliance with tax laws and regulations.
Many ATGs target specific industries, such as construction, aerospace, art galleries, architecture and veterinary medicine. Other guides address issues that frequently arise in audits, such as executive compensation, passive activity losses and capitalization of tangible property.
IRS auditors need to examine all different types of businesses, as well as individual taxpayers and tax-exempt organizations. Each type of return might have unique industry issues, business practices and terminology. Before meeting with taxpayers and their advisors, auditors do their homework to understand various industries or issues, the accounting methods commonly used, how income is received, and areas where taxpayers might not be in compliance.
By using a specific ATG, an IRS auditor may be able to reconcile discrepancies when reported income or expenses aren’t consistent with what’s normal for the industry or to identify anomalies within the geographic area in which the business is located.
Some guides were written several years ago and others are relatively new. There isn’t a guide for every industry. Here are some of the guide titles that have been revised or added in recent years:
Although ATGs were created to help IRS examiners uncover common methods of hiding income and inflating deductions, they also can help businesses ensure they aren’t engaging in practices that could raise audit red flags. For a complete list of ATGs, visit the IRS website.
© 2023
Owning a business is an exciting journey filled with highs and lows. Establishing a clear, profit-driven strategy is one key factor that can tilt the scales toward success. The recent tax court case, Gregory v. Commissioner, highlighted how blurring the lines between hobbies and genuine business ventures can have significant financial implications. Not only did this case underscore the importance of clear delineation, but it also highlighted the potential tax pitfalls of not doing so. In this article, we’ll cover how to ensure your venture is seen as a legitimate business and not just a pricey pastime.
The “hobby loss” rules have made waves in the tax world, affecting many business activities, from horse breeding to charter boat operations and even Airbnb rentals. Only activities classified as what the IRS refers to as “engaged in for profit” are able to deduct expenses associated with the work. In other words, to be considered “engaged in for profit” means you set out with the intention of your business and activity to generate a profit. If the IRS determines the activity was not “engaged in for profit,” your ability to deduct associated expenses will be impacted. If your venture is potentially labeled a hobby, you could find yourself in a situation where you’re reporting full income without the benefit of crucial deductions.
In the case of Gregory discussed above, the business owner reported gross income equaling the business expenses, yet he couldn’t use the deductions due to the hobby classification. As a result, the ruling reduced his profit and increased the business’s taxes due, which is not the ideal scenario for any business owner.
The U.S. Tax Court and the Internal Revenue Service use a range of factors to determine whether a business truly has a profit motive. Remember, while starting a business around your passion is fantastic, the profit motive is what separates it as a sustainable business rather than an expensive hobby.
Four steps can make it a clear and recurrent theme in your business strategy.
When your business displays a consistent profit-driven strategy, you’re protecting yourself from potential tax pitfalls and setting your venture up for long-term success. Adhering to these guidelines reflects solid business judgment that can benefit your company in the long run. Remember the consequences: a misclassified hobby can lead to reporting full income without deducing the expenses.
Are you currently engaged in a business activity that could toe the line between hobby and legitimate venture? Chat with your tax advisor. Discuss your profit-driven strategies and plans, taking lessons from the Gregory case. Continual reflection and adaptation, even in the face of enjoyable or recreational activities, are the keys to solidifying your business’s market placement.
The line between passion and profit is a fine one. Yet, with a clear, profit-driven strategy and awareness of nuances like the “hobby loss” rules, you can ensure your business thrives in today’s competitive marketplace. Stay informed, stay adaptable, and always keep that profit motive at the forefront of your business operations.
As of Sept. 14, 2023, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) announced an immediate halt to the processing of new claims for the Employee Retention Credit (ERC) program. This decision is effective until at least the end of the current year. It comes in response to a significant influx of questionable ERC claims.
The IRS has raised serious concerns about scams targeting honest small business owners. Reports suggest that many businesses, influenced by what the IRS termed aggressive marketing tactics, are applying for credits they’re not eligible for. Such questionable claims endanger businesses’ financial stability and put undue strain on the tax system. The intention behind this moratorium is to protect businesses and the integrity of the tax system from predatory tactics and fraudulent claims.
The IRS’s increasing focus on reviewing these claims for compliance has led to a substantial number of audits and criminal investigations. Their collaboration with the Justice Department aims to address and reduce the number of fraudulent claims and to tackle promoters pushing businesses toward such actions.
Based on what we know right now, here is how this halt might affect you as a small business owner:
The IRS has said they will provide more details on various initiatives in the upcoming fall season—including more information on the settlement program, allowing businesses to repay any mistakenly received ERC funds without incurring penalties.
This moratorium underscores the need for businesses to be vigilant and informed. In times of crisis, while relief measures like the ERC are invaluable, they can also become fertile ground for scams and misinformation. Ensure your business is protected from these threats by staying informed and seeking advice from trusted professionals.
If you read the Internal Revenue Code (and you probably don’t want to!), you may be surprised to find that most business deductions aren’t specifically listed. For example, the tax law doesn’t explicitly state that you can deduct office supplies and certain other expenses. Some expenses are detailed in the tax code, but the general rule is contained in the first sentence of Section 162, which states you can write off “all the ordinary and necessary expenses paid or incurred during the taxable year in carrying on any trade or business.”
In general, an expense is ordinary if it’s considered common or customary in the particular trade or business. For example, insurance premiums to protect a store would be an ordinary business expense in the retail industry.
A necessary expense is defined as one that’s helpful or appropriate. For example, let’s say a car dealership purchases an automated external defibrillator. It may not be necessary for the operation of the business, but it might be helpful and appropriate if an employee or customer suffers cardiac arrest.
It’s possible for an ordinary expense to be unnecessary — but, in order to be deductible, an expense must be ordinary and necessary.
In addition, a deductible amount must be reasonable in relation to the benefit expected. For example, if you’re attempting to land a $3,000 deal, a $65 lunch with a potential client should be OK with the IRS. (Keep in mind that the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act eliminated most deductions for entertainment expenses but retained the 50% deduction for business meals.)
Not surprisingly, the IRS and courts don’t always agree with taxpayers about what qualifies as ordinary and necessary expenditures. Here are three 2023 cases to illustrate some of the issues:
The deductibility of some expenses is clear. But for other expenses, it can get more complicated. Generally, if an expense seems like it’s not normal in your industry — or if it could be considered fun, personal or extravagant in nature — you should proceed with caution. And keep careful records to substantiate the expenses you’re deducting. Consult with us for guidance.
©️ 2023
Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines affecting businesses and other employers during the fourth quarter of 2023. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. Contact us to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines and to learn more about the filing requirements.
Note: Certain tax-filing and tax-payment deadlines may be postponed for taxpayers who reside in or have businesses in federally declared disaster areas.
Contact us if you’d like more information about the filing requirements and to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines.
© 2023
In recent years, merger and acquisition activity has been strong in many industries. If your business is considering merging with or acquiring another business, it’s important to understand how the transaction will be taxed under current law.
From a tax standpoint, a transaction can basically be structured in two ways:
The now-permanent 21% corporate federal income tax rate under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) makes buying the stock of a C corporation somewhat more attractive. Reasons: The corporation will pay less tax and generate more after-tax income. Plus, any built-in gains from appreciated corporate assets will be taxed at a lower rate when they’re eventually sold.The TCJA’s reduced individual federal tax rates may also make ownership interests in S corporations, partnerships and LLCs more attractive. Reason: The passed-through income from these entities also will be taxed at lower rates on a buyer’s personal tax return. However, the TCJA’s individual rate cuts are scheduled to expire at the end of 2025, and, depending on future changes in Washington, they could be eliminated earlier or extended.
Note: In some circumstances, a corporate stock purchase can be treated as an asset purchase by making a “Section 338 election.” Ask us if this would be beneficial in your situation.
For several reasons, buyers usually prefer to purchase assets rather than ownership interests. Generally, a buyer’s main objective is to generate enough cash flow from an acquired business to pay any acquisition debt and provide an acceptable return on the investment. Therefore, buyers are concerned about limiting exposure to undisclosed and unknown liabilities and minimizing taxes after the deal closes.
A buyer can step up (increase) the tax basis of purchased assets to reflect the purchase price. Stepped-up basis lowers taxable gains when certain assets, such as receivables and inventory, are sold or converted into cash. It also increases depreciation and amortization deductions for qualifying assets.
Meanwhile, sellers generally prefer stock sales for tax and nontax reasons. One of their main objectives is to minimize the tax bill from a sale. That can usually be achieved by selling their ownership interests in a business (corporate stock, or partnership or LLC interests) as opposed to selling business assets.
With a sale of stock or other ownership interest, liabilities generally transfer to the buyer and any gain on sale is generally treated as lower-taxed long-term capital gain (assuming the ownership interest has been held for more than one year).
Keep in mind that other areas, such as employee benefits, can also cause unexpected tax issues when merging with, or acquiring, a business.
Buying or selling a business may be the most important transaction you make during your lifetime, so it’s important to seek professional tax advice as you negotiate. After a deal is done, it may be too late to get the best tax results. Contact us for the best way to proceed.
© 2023
In an era of growing environmental awareness and the push for sustainable living, homeowners are more interested than ever in upgrading their living spaces to be energy-efficient. However, it’s not just about saving the planet—it’s also about saving money. The U.S. government, recognizing the importance of these measures, has provided an enticing incentive: The Energy-Efficient Home Improvement Credit. Here’s everything you need to know about this tax relief opportunity.
The Energy-Efficient Home Improvement Credit is an initiative by the IRS designed to encourage homeowners to make eco-friendly home upgrades. If you have made any qualifying energy-efficient improvements to your home since January 1, 2023, you may be eligible for this credit, where the savings could be substantial.
The first step in determining eligibility is determining what improvements qualify. The following energy-efficient improvements, when in line with requirements set on energy.gov, can make you eligible for the credit:
Once you have determined which improvements qualify, you might wonder what the savings could be if you claimed the credit. The potential savings can be significant. Here’s a breakdown:
The silver lining? There is no lifetime dollar limit on this credit. If you make eligible improvements annually, you can claim the maximum amount every year until 2033.
If you use your home for business, there are special considerations where you could be eligible to claim a percentage of the credit, even 100%.
If this applies to you, it is best to talk with an accountant about the most beneficial use of this credit.
Here are some essential pointers to keep in mind:
While making your home more energy-efficient is a commendable step toward sustainability, it also offers financial benefits. The Energy-Efficient Home Improvement Credit is an avenue worth exploring for homeowners. By staying informed and making timely upgrades, you can contribute to a greener planet and enjoy tangible tax savings.
Are you wondering if your energy-efficient choices will qualify for this tax credit? Hamilton Tharp is here to help. Reach out to us, and let’s map out a greener, cost-efficient future for your home.
For more details and regular updates, keep an eye on Hamilton Tharp’s insights on tax savings and financial strategies.
Do you and your spouse together operate a profitable unincorporated small business? If so, you face some challenging tax issues.
An unincorporated business with your spouse is classified as a partnership for federal income tax purposes, unless you can avoid that treatment. Otherwise, you must file an annual partnership return, on Form 1065. In addition, you and your spouse must be issued separate Schedule K-1s, which allocate the partnership’s taxable income, deductions and credits between the two of you. This is only the beginning of the unwelcome tax compliance tasks.
The SE tax is how the government collects Social Security and Medicare taxes from self-employed individuals. For 2023, the SE tax consists of 12.4% Social Security tax on the first $160,200 of net SE income plus 2.9% Medicare tax. Once your 2023 net SE income surpasses the $160,200 ceiling, the Social Security tax component of the SE tax ends. But the 2.9% Medicare tax component continues before increasing to 3.8% — thanks to the 0.9% additional Medicare tax — if the combined net SE income of a married joint-filing couple exceeds $250,000.
With your joint Form 1040, you must include a Schedule SE to calculate SE tax on your share of the net SE income passed through to you by your spousal partnership. The return must also include a Schedule SE for your spouse to calculate the tax on your spouse’s share of net SE income passed through to him or her. This can result in a big SE tax bill.
For example, let’s say you and your spouse each have net 2023 SE income of $150,000 ($300,000 total) from your profitable 50/50 partnership business. The SE tax on your joint tax return is a whopping $45,900 ($150,000 x 15.3% x 2). That’s on top of regular federal income tax.
Strategy 1: Use an IRS-approved method to minimize SE tax in a community property state
Under IRS Revenue Procedure 2002-69, for federal tax purposes, you can treat an unincorporated spousal business in a community property state as a sole proprietorship operated by one of the spouses. By effectively allocating all the net SE income to the proprietor spouse, only the first $160,200 of net SE income is hit with the 12.4% Social Security tax. That can cut your SE tax bill.
Strategy 2: Convert a spousal partnership into an S corporation and pay modest salaries
If you and your unincorporated spousal business aren’t in a community property state, consider converting the business to S corporation status to reduce Social Security and Medicare taxes. That way, only the salaries paid to you and your spouse get hit with the Social Security and Medicare tax, collectively called FICA tax. You can then pay modest, but reasonable, salaries to you and your spouse as shareholder-employees while paying out most or all remaining corporate cash flow to yourselves as FICA-tax-free cash distributions.
Strategy 3: Disband your partnership and hire your spouse as an employee
You can disband the existing spousal partnership and start running the operation as a sole proprietorship operated by one spouse. Then hire the other spouse as an employee of the proprietorship. Pay that spouse a modest cash salary. You must withhold 7.65% from the salary to cover the employee-spouse’s share of the Social Security and Medicare taxes. The proprietorship must also pay 7.65% as the employer’s half of the taxes. However, since the employee-spouse’s salary is modest, the FICA tax will also be modest.
With this strategy, you file only one Schedule SE — for the spouse treated as the proprietor — with your joint tax return. That minimizes the SE tax, because no more than $160,200 (for 2023) is exposed to the 12.4% Social Security portion of the SE tax.
Having a profitable unincorporated business with your spouse that’s classified as a partnership for federal income tax purposes can lead to compliance headaches and high SE tax bills. Work with us to identify appropriate tax-saving strategies.
© 2023
The IRS announced that it has stopped processing all new Employee Retention Credit (ERC) refund claims and will continue its moratorium at least through December 31, 2023. (IR-2023-169)
In IRS Commissioner Werfel’s words:
“The IRS is increasingly alarmed about honest small business owners being scammed by unscrupulous actors, and we could no longer tolerate growing evidence of questionable claims pouring in… The continued aggressive marketing of these schemes is harming well-meaning businesses and delaying the payment of legitimate claims, which makes it harder to run the rest of the tax system.”
The IRS is continuing to process ERC claims filed prior to the 09/14/2023 announcement, but even those claims will face long processing delays (up to 180 days from 90 days) because the IRS is placing stricter compliance reviews on all claims. The IRS is developing a new settlement program for taxpayers who received an improper ERC payment that should be available later in Fall 2023.
The IRS’s release is available HERE and contains advice for taxpayers whose ERC claims may be in various stages.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act liberalized the rules for depreciating business assets. However, the amounts change every year due to inflation adjustments. And due to high inflation, the adjustments for 2023 were big. Here are the numbers that small business owners need to know.
For qualifying assets placed in service in tax years beginning in 2023, the maximum Sec. 179 deduction is $1.16 million. But if your business puts in service more than $2.89 million of qualified assets, the maximum Sec. 179 deduction begins to be phased out.
Eligible assets include depreciable personal property such as equipment, computer hardware and peripherals, vehicles and commercially available software.
Sec. 179 deductions can also be claimed for real estate qualified improvement property (QIP), up to the maximum allowance of $1.16 million. QIP is defined as an improvement to an interior portion of a nonresidential building placed in service after the date the building was placed in service. However, expenditures attributable to the enlargement of a building, elevators or escalators, or the internal structural framework of a building don’t count as QIP and usually must be depreciated over 39 years. There’s no separate Sec. 179 deduction limit for QIP, so deductions reduce your maximum allowance dollar for dollar.
For nonresidential real property, Sec. 179 deductions are also allowed for qualified expenditures for roofs, HVAC equipment, fire protection and alarm systems, and security systems.
Finally, eligible assets include depreciable personal property used predominantly in connection with furnishing lodging, such as furniture and appliances in a property rented to transients.
There’s a special limitation on Sec. 179 deductions for heavy SUVs, meaning those with gross vehicle weight ratings (GVWR) between 6,001 and 14,000 pounds. For tax years beginning in 2023, the maximum Sec. 179 deduction for heavy SUVs is $28,900.
For qualified new and used assets that were placed in service in calendar year 2022, 100% first-year bonus depreciation percentage could be claimed.
However, for qualified assets placed in service in 2023, the first-year bonus depreciation percentage dropped to 80%. In 2024, it’s scheduled to drop to 60% (40% in 2025, 20% in 2026 and 0% in 2027 and beyond).
Eligible assets include depreciable personal property such as equipment, computer hardware and peripherals, vehicles and commercially available software. First-year bonus depreciation can also be claimed for real estate QIP.
Exception: For certain assets with longer production periods, these percentage cutbacks are delayed by one year. For example, the 80% depreciation rate will apply to long-production-period property placed in service in 2024.
For federal income tax depreciation purposes, passenger autos are defined as cars, light trucks and light vans. These vehicles are subject to special depreciation limits under the so-called luxury auto depreciation rules. For new and used passenger autos placed in service in 2023, the maximum luxury auto deductions are as follows:
These allowances assume 100% business use. They’ll be further adjusted for inflation in future years.
Heavy SUVs, pickups, and vans (those with GVWRs above 6,000 pounds) are exempt from the luxury auto depreciation limitations because they’re considered transportation equipment. As such, heavy vehicles are eligible for Sec. 179 deductions (subject to the special deduction limit explained earlier) and first-year bonus depreciation.
Here’s the catch: Heavy vehicles must be used over 50% for business. Otherwise, the business-use percentage of the vehicle’s cost must be depreciated using the straight-line method and it’ll take six tax years to fully depreciate the cost.
Consult with us for the maximum depreciation tax breaks in your situation.
© 2023
California State Law requires employers who reported having an average of 5 or more employees in 2022 to register for CalSavers unless they meet one of the conditions for exemption:
Employers will start receiving their official registration information by US mail and email. If you believe your company is exempt from the mandate, submit an exemption request.
Registration/Exemption Deadline: December 31, 2023 for 5 or more employees.
In 2022, California passed legislation (SB 1126) to expand the CalSavers mandate to employers with at least one employee. Starting on January 1, 2023, employers with 1-4 employees (as reported to the EDD in the preceding calendar year) who are not otherwise exempt from participation can register with CalSavers.
Registration/Exemption Deadline: December 31, 2025 for 1-4 employees
In business, where every decision can tip the scales of success or failure, a robust financial strategy is imperative. Enter Financial Planning & Analysis (FP&A) – an often underappreciated yet pivotal function that can revolutionize how businesses plan, analyze, and project their financial future.
What exactly is FP&A? At its core, FP&A serves as the bridge between strategic planning and its execution. It’s the analytical arm of the finance department, scrutinizing past performances and forecasting future trends. While traditional accounting looks backward, detailing where a company has been, FP&A looks forward, charting where it’s headed. It complements the accounting function by bringing an analytical and predictive dimension to the table. Together, they provide a holistic view of a company’s financial health.
FP&A is more than a tool reserved for accountants or financial experts. It’s an invaluable financial guide that acts as a compass for every entrepreneur and project manager. This financial guide offers:
By analyzing financial trends, FP&A drives strategic direction, ensures profitable revenues, and assists in budgeting and forecasting. It’s no wonder that businesses integrating FP&A report a 30% increase in forecast accuracy.
The business world is in constant flux. The days of static annual reviews have been left behind. With rapidly changing market dynamics, agility in financial planning isn’t a luxury—it’s a necessity. This fluid approach ensures that businesses remain proactive, ready to seize opportunities or avoid impending challenges.
Steps to Seamlessly Integrate FP&A in Project Planning
By understanding the nuances of FP&A and weaving it into business processes, companies can make informed decisions, minimize risks, and amplify profitability. In the unpredictable world of modern commerce, FP&A stands as a trusted compass, guiding firms towards a brighter future.
Inheritance brings its own set of challenges. Within the vast world of financial legacies, inherited Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) stand out thanks to their annual withdrawal requirements, also known as Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs). With these RMDs comes the caveat of taxation. However, when the Secure Act of 2019 was introduced, it brought clarity and confusion, mainly by introducing new beneficiary categories.
The Secure Act ushered in three beneficiary categories, each with distinct withdrawal rules:
Many beneficiaries, particularly NEDBs, found these rules intricate. The real task was classifying themselves correctly and adhering to the associated RMD rules to avoid tax penalties.
In response to the confusion stemming from the Secure Act’s implementation, the IRS released Notice 2022-53 in October 2022. For those beneficiaries whose original IRA owner had begun their RMDs, they must commence their own RMDs in the year following the owner’s passing. Furthermore, the complete balance should be dispensed by the 10th year after the owner’s death.
Recognizing the challenges arising from the Secure Act, the IRS also waived penalties for NEDBs who missed RMDs in 2021 and 2022 to show its commitment to assist during these regulatory transitions.
Things to remember:
To navigate the inherited IRA terrain confidently, beneficiaries should:
Although financial regulations seem intimidating, beneficiaries can efficiently manage their inherited IRAs with the right guidance and proactive approach. By understanding their specific obligations under the Secure Act and seeking expert advice, beneficiaries can comply with regulations and make informed decisions that honor their inheritances and bolster their financial futures.
If you’re getting a divorce, you know the process is generally filled with stress. But if you’re a business owner, tax issues can complicate matters even more. Your business ownership interest is one of your biggest personal assets and in many cases, your marital property will include all or part of it.
In general, you can divide most assets, including cash and business ownership interests, between you and your soon-to-be ex-spouse without any federal income or gift tax consequences. When an asset falls under this tax-free transfer rule, the spouse who receives the asset takes over its existing tax basis (for tax gain or loss purposes) and its existing holding period (for short-term or long-term holding period purposes).
For example, let’s say that under the terms of your divorce agreement, you give your house to your spouse in exchange for keeping 100% of the stock in your business. That asset swap would be tax-free. And the existing basis and holding period for the home and the stock would carry over to the person who receives them.
Tax-free transfers can occur before a divorce or at the time it becomes final. Tax-free treatment also applies to post-divorce transfers as long as they’re made “incident to divorce.” This means transfers that occur within:
Eventually, there will be tax implications for assets received tax-free in a divorce settlement. The ex-spouse who winds up owning an appreciated asset — when the fair market value exceeds the tax basis — generally must recognize taxable gain when it’s sold (unless an exception applies).
What if your ex-spouse receives 49% of your highly appreciated small business stock? Thanks to the tax-free transfer rule, there’s no tax impact when the shares are transferred. Your ex will continue to apply the same tax rules as if you had continued to own the shares, including carryover basis and carryover holding period. When your ex-spouse ultimately sells the shares, he or she will owe any capital gains taxes. You will owe nothing.
Note: The person who winds up owning appreciated assets must pay the built-in tax liability that comes with them. From a net-of-tax perspective, appreciated assets are worth less than an equal amount of cash or other assets that haven’t appreciated. That’s why you should always take taxes into account when negotiating your divorce agreement.
In addition, the beneficial tax-free transfer rule is now extended to ordinary-income assets, not just to capital-gains assets. For example, if you transfer business receivables or inventory to your ex-spouse in a divorce, these types of ordinary-income assets can also be transferred tax-free. When the asset is later sold, converted to cash or exercised (in the case of nonqualified stock options), the person who owns the asset at that time must recognize the income and pay the tax liability.
Like many major life events, divorce can have significant tax implications. For example, you may receive an unexpected tax bill if you don’t carefully handle the splitting up of qualified retirement plan accounts (such as a 401(k) plan) and IRAs. And if you own a business, the stakes are higher. Contact us. We can help you minimize the adverse tax consequences of settling your divorce.
© 2023
Let’s say you decide to, or are asked to, guarantee a loan to your corporation. Before agreeing to act as a guarantor, endorser or indemnitor of a debt obligation of your closely held corporation, be aware of the possible tax implications. If your corporation defaults on the loan and you’re required to pay principal or interest under the guarantee agreement, you don’t want to be caught unaware.
If you’re compelled to make good on the obligation, the payment of principal or interest in discharge of the obligation generally results in a bad debt deduction. This may be either a business or a nonbusiness bad debt deduction. If it’s a business bad debt, it’s deductible against ordinary income. A business bad debt can be either totally or partly worthless. If it’s a nonbusiness bad debt, it’s deductible as a short-term capital loss, which is subject to certain limitations on deductions of capital losses. A nonbusiness bad debt is deductible only if it’s totally worthless.
In order to be treated as a business bad debt, the guarantee must be closely related to your trade or business. If the reason for guaranteeing the corporation loan is to protect your job, the guarantee is considered closely related to your trade or business as an employee. But employment must be the dominant motive. If your annual salary exceeds your investment in the corporation, this generally shows that the dominant motive for the guarantee was to protect your job. On the other hand, if your investment in the corporation substantially exceeds your annual salary, that’s evidence that the guarantee was primarily to protect your investment rather than your job.
Except in the case of job guarantees, it may be difficult to show the guarantee was closely related to your trade or business. You’d have to show that the guarantee was related to your business as a promoter, or that the guarantee was related to some other trade or business separately carried on by you.
If the reason for guaranteeing your corporation’s loan isn’t closely related to your trade or business and you’re required to pay off the loan, you can take a nonbusiness bad debt deduction if you show that your reason for the guarantee was to protect your investment, or you entered the guarantee transaction with a profit motive.
In addition to satisfying the above requirements, a business or nonbusiness bad debt is deductible only if you meet these three requirements:
Any payment you make on a loan you guaranteed is deductible as a bad debt in the year you make it, unless the agreement (or local law) provides for a right of subrogation against the corporation. If you have this right, or some other right to demand payment from the corporation, you can’t take a bad debt deduction until the rights become partly or totally worthless.
These are only some of the possible tax consequences of guaranteeing a loan to your closely held corporation. To learn all the implications in your situation, consult with us.
© 2023
The SECURE 2.0 law, which was enacted last year, contains wide-ranging changes to retirement plans. One provision in the law is that eligible employers will soon be able to provide more help to staff members facing emergencies. This will be done through what the law calls “pension-linked emergency savings accounts.”
Effective for plan years beginning January 1, 2024, SECURE 2.0 permits a plan sponsor to amend its 401(k), 403(b) or government 457(b) plan to offer emergency savings accounts that are connected to the plan.
If a retirement plan participant withdraws money from an employer plan before reaching age 59½, a 10% additional tax or penalty generally applies unless an exception exists. This is on top of the ordinary tax that may be due.
The goal of these emergency accounts is to encourage employees to save for retirement while still providing access to their savings if emergencies arise. Under current law, there are specific exceptions when employees can withdraw money from their accounts without paying the additional 10% penalty but they don’t include all of the emergencies that an individual may face. For example, while participants can take penalty-free distributions to pay eligible medical expenses, they can’t take them for car repairs.
Here are some features of pension-linked emergency savings accounts:
In addition to these accounts, SECURE 2.0 adds a new exception for certain retirement plan distributions used for emergency expenses, which are defined as unforeseeable or immediate financial needs relating to personal or family emergencies. Only one distribution of up to $1,000 is permitted a year, and a taxpayer has the option to repay the distribution within three years. This provision is effective for distributions beginning January 1, 2024.
In addition to what is outlined here, other rules apply to pension-linked emergency savings accounts. The IRS is likely to issue additional guidance in the next few months. Be aware that plan sponsors don’t have to offer these accounts and many employers may find that they need more time to establish them before 2024. Or they may decide there are too many administrative hurdles to clear. Contact us with questions.
© 2023
Does your business receive large amounts of cash or cash equivalents? If so, you’re generally required to report these transactions to the IRS — and not just on your tax return.
Each person who, in the course of operating a trade or business, receives more than $10,000 in cash in one transaction (or two or more related transactions), must file Form 8300. Who is a “person”? It can be an individual, company, corporation, partnership, association, trust or estate. What are considered “related transactions”? Any transactions conducted in a 24-hour period. Transactions can also be considered related even if they occur over a period of more than 24 hours if the recipient knows, or has reason to know, that each transaction is one of a series of connected transactions.
In order to complete a Form 8300, you’ll need personal information about the person making the cash payment, including a Social Security or taxpayer identification number.
For Form 8300 reporting purposes, cash includes U.S. currency and coins, as well as foreign money. It also includes cash equivalents such as cashier’s checks (sometimes called bank checks), bank drafts, traveler’s checks and money orders.
Money orders and cashier’s checks under $10,000, when used in combination with other forms of cash for a single transaction that exceeds $10,000, are defined as cash for Form 8300 reporting purposes.
Note: Under a separate reporting requirement, banks and other financial institutions report cash purchases of cashier’s checks, treasurer’s checks and/or bank checks, bank drafts, traveler’s checks and money orders with a face value of more than $10,000 by filing currency transaction reports.
Although many cash transactions are legitimate, the IRS explains that the information reported on Form 8300 “can help stop those who evade taxes, profit from the drug trade, engage in terrorist financing and conduct other criminal activities. The government can often trace money from these illegal activities through the payments reported on Form 8300 and other cash reporting forms.”
Failing to comply with the law can result in fines and even jail time. In one case, a Niagara Falls, NY, business owner was convicted of willful failure to file Form 8300 after receiving cash transactions of more than $10,000. In a U.S. District Court, he pled guilty and was recently sentenced to five months home detention, fined $10,000 and he agreed to pay restitution to the IRS. He had received cash rent payments in connection with a building in which he had an ownership interest.
Businesses required to file reports of large cash transactions on Forms 8300 should know that in addition to filing on paper, e-filing is an option. The form is due 15 days after a transaction and there’s no charge for the e-file option. Businesses that file electronically get an automatic confirmation of receipt when they file.
Effective January 1, 2024, you may have to e-file Forms 8300 if you’re required to e-file other information returns, such as 1099 and W-2 forms. You must e-file if you’re required to file at least 10 information returns other than Form 8300 during a calendar year.
The IRS also reminds businesses that they can “batch file” their reports, which is especially helpful to those required to file many forms.
You should keep a copy of each Form 8300 for five years from the date you file it, according to the IRS. “Confirmation receipts don’t meet the recordkeeping requirement,” the tax agency added.
Contact us with any questions or for assistance.
© 2023
As a business owner, your goal is to ensure your venture thrives and prospers. An essential aspect of this journey involves maintaining a clear, accurate financial perspective that allows you to make informed decisions. But what happens when accounting errors creep into this clear vision? These unintentional mistakes can significantly hinder your business’s growth and profitability.
By understanding these errors, their implications, and ways to prevent them, you can maintain the financial health of your organization and keep your business on a growth trajectory. This article delves into common accounting errors that impede business growth and how to avoid them.
Accounting errors are unintentional inaccuracies in your financial books. These can be clerical mistakes or incorrect applications of accounting principles, ranging from duplicate entries to record omissions. While they may seem minor, these errors can lead to significant financial discrepancies, skew your business’s financial health perception, and potentially impede growth.
Several common types of accounting errors can negatively affect your business. Let’s look at a few of the common errors, and what the effects could be:
Common Errors |
|
|
Error of Original Entry |
when an incorrect amount is posted to an account, which could result in skewed financial reports and affect your decision-making. |
|
Errors of Duplication |
lead to incorrect perceptions of expenses. |
| Errors of Omission | could cause under-reporting of your liabilities or income. |
| Errors of Entry Reversal | where debits are recorded as credits and vice versa, can affect your understanding of financial position and performance. |
| Errors of Principle | which involve misapplication of accounting principles, can lead to misclassification of your expenses or assets. |
| Error of Commission | happens when an entry is posted correctly to an account but incorrectly to a subsidiary account, creating confusion and mismanagement of client accounts or vendor payments. |
|
Compensating Errors |
where one error offsets another, can mask actual problems, leading to potential financial crises. |
Recognizing and rectifying accounting errors in your business operations holds immense value. For example:
Perhaps most critically, it safeguards your business against potential financial crises by unmasking issues that may otherwise be hidden. Proactively identifying and addressing accounting errors is a proactive step toward financial accuracy, operational efficiency, and sustainable business growth.
Now that we understand the potential pitfalls, let’s focus on how you can prevent these errors from stunting your business’s growth.
While keeping these errors at bay may seem challenging, remember that every step toward error-free accounting is a step toward your business’s sustainable growth.
Accounting errors can be more than a mere annoyance. They can obscure the financial health of your business, leading to misinformed decisions and hindering growth. By understanding and preventing these errors, you safeguard your financial records and gain reliable insights to propel your business forward. Remember, an accurate financial perspective is key to informed decision-making and, ultimately, the success of your venture.
If you operate your small business as a sole proprietorship, you may have thought about forming a limited liability company (LLC) to protect your assets. Or maybe you’re launching a new business and want to know your options for setting it up. Here are the basics of operating as an LLC and why it might be a good choice for your business.
An LLC is a bit of a hybrid entity because it can be structured to resemble a corporation for owner liability purposes and a partnership for federal tax purposes. This duality may provide the owners with the best of both worlds.
Like the shareholders of a corporation, the owners of an LLC (called “members” rather than shareholders or partners) generally aren’t liable for the debts of the business except to the extent of their investment. Thus, the owners can operate the business with the security of knowing that their personal assets are protected from the entity’s creditors. This protection is much greater than that afforded by partnerships. In a partnership, the general partners are personally liable for the debts of the business. Even limited partners, if they actively participate in managing the business, can have personal liability.
The owners of an LLC can elect under the “check-the-box” rules to have the entity treated as a partnership for federal tax purposes. This can provide a number of benefits to the owners. For example, partnership earnings aren’t subject to an entity-level tax. Instead, they “flow through” to the owners, in proportion to the owners’ respective interests in profits, and are reported on the owners’ individual returns and taxed only once.
To the extent the income passed through to you is qualified business income, you’ll be eligible to take the Section 199A pass-through deduction, subject to various limitations. (However, keep in mind that the pass-through deduction is temporary. It’s available through 2025, unless Congress acts to extend it.)
In addition, since you’re actively managing the business, you can deduct on your individual tax return your ratable shares of any losses the business generates. This, in effect, allows you to shelter other income that you (and your spouse, if you’re married) may have.
An LLC that’s taxable as a partnership can provide special allocations of tax benefits to specific partners. This can be a notable reason for using an LLC over an S corporation (a form of business that provides tax treatment that’s similar to a partnership). Another reason for using an LLC over an S corp is that LLCs aren’t subject to the restrictions the federal tax code imposes on S corps regarding the number of owners and the types of ownership interests that may be issued.
In conclusion, an LLC can give you corporate-like protection from creditors while providing the benefits of taxation as a partnership. For these reasons, you may want to consider operating your business as an LLC. Contact us to discuss in more detail how an LLC might be an appropriate choice for you and the other owners.
© 2023
Let’s say you own highly appreciated land that’s now ripe for development. If you subdivide it, develop the resulting parcels and sell them off for a hefty profit, it could trigger a large tax bill.
In this scenario, the tax rules generally treat you as a real estate dealer. That means your entire profit — including the portion from pre-development appreciation in the value of the land — will be treated as high-taxed ordinary income subject to a federal rate of up to 37%. You may also owe the 3.8% net investment income tax (NIIT) for a combined federal rate of up to 40.8%. And you may owe state income tax too.
It would be better if you could arrange to pay lower long-term capital gain (LTCG) tax rates on at least part of the profit. The current maximum federal income tax rate on LTCGs is 20% or 23.8% if you owe the NIIT.
Thankfully, there’s a strategy that allows favorable LTCG tax treatment for all pre-development appreciation in the land value. You must have held the land for more than one year for investment (as opposed to holding it as a real estate dealer).
The portion of your profit attributable to subsequent subdividing, development and marketing activities will still be considered high-taxed ordinary income, because you’ll be considered a real estate dealer for that part of the process.
But if you can manage to pay a 20% or 23.8% federal income tax rate on a big chunk of your profit (the pre-development appreciation part), that’s something to celebrate.
Here’s the three-step strategy that could result in paying a smaller tax bill on your real estate development profits.
If you individually own the appreciated land, you can establish an S corporation owned solely by you to function as the developer. If you own the land via a partnership, or via an LLC treated as a partnership for federal tax purposes, you and the other partners (LLC members) can form the S corp and receive corporate stock in proportion to your percentage partnership (LLC) interests.
Sell the appreciated land to the S corp for a price equal to the land’s pre-development fair market value. If necessary, you can arrange a sale that involves only a little cash and a big installment note the S corp owes you. The business will pay off the note with cash generated by selling off parcels after development. The sale to the S corp will trigger a LTCG eligible for the 20% or 23.8% rate as long as you held the land for investment and owned it for over one year.
The S corp will subdivide and develop the property, market it and sell it off. The profit from these activities will be higher-taxed ordinary income passed through to you as an S corp shareholder. If the profit is big, you’ll probably pay the maximum 37% federal rate (or 40.8% percent with the NIIT. However, the average tax rate on your total profit will be much lower, because a big part will be lower-taxed LTCG from pre-development appreciation.
Thanks to the tax treatment created by this S corp developer strategy, you can lock in favorable treatment for the land’s pre-development appreciation. That’s a huge tax-saving advantage if the land has gone up in value. Consult with us if you have questions or want more information.
© 2023
If you play a major role in a closely held corporation, you may sometimes spend money on corporate expenses personally. These costs may end up being nondeductible both by an officer and the corporation unless the correct steps are taken. This issue is more likely to happen with a financially troubled corporation.
In general, you can’t deduct an expense you incur on behalf of your corporation, even if it’s a legitimate “trade or business” expense and even if the corporation is financially troubled. This is because a taxpayer can only deduct expenses that are his own. And since your corporation’s legal existence as a separate entity must be respected, the corporation’s costs aren’t yours and thus can’t be deducted even if you pay them.
To make matters worse, the corporation won’t generally be able to deduct them either because it didn’t pay them itself. Accordingly, be advised that it shouldn’t be a practice of your corporation’s officers or major shareholders to cover corporate costs.
On the other hand, if a corporate executive incurs costs that relate to an essential part of his or her duties as an executive, they may be deductible as ordinary and necessary expenses related to his or her “trade or business” of being an executive. If you wish to set up an arrangement providing payments to you and safeguarding their deductibility, a provision should be included in your employment contract with the corporation stating the types of expenses which are part of your duties and authorizing you to incur them. For example, you may be authorized to attend out-of-town business conferences on the corporation’s behalf at your personal expense.
Alternatively, to avoid the complete loss of any deductions by both yourself and the corporation, an arrangement should be in place under which the corporation reimburses you for the expenses you incur. Turn the receipts over to the corporation and use an expense reimbursement claim form or system. This will at least allow the corporation to deduct the amount of the reimbursement.
Contact us if you’d like assistance or would like to discuss these issues further.
© 2023
If you own an unincorporated small business, you probably don’t like the size of your self-employment (SE) tax bills. No wonder!
For 2023, the SE tax is imposed at the painfully high rate of 15.3% on the first $160,200 of net SE income. This includes 12.4% for Social Security tax and 2.9% for Medicare tax. The $160,200 Social Security tax ceiling is up from the $147,000 ceiling for 2022, and it’s only going to get worse in future years, thanks to inflation. Above the Social Security tax ceiling, the Medicare tax component of the SE tax continues at a 2.9% rate before increasing to 3.8% at higher levels of net SE income thanks to the 0.9% additional Medicare tax, on all income.
For wages paid in 2023 to an S corporation employee, including an employee who also happens to be a shareholder, the FICA tax wage withholding rate is 7.65% on the first $160,200 of wages: 6.2% for Social Security tax and 1.45% for Medicare tax. Above $160,200, the FICA tax wage withholding rate drops to 1.45% because the Social Security tax component is no longer imposed. But the 1.45% Medicare tax wage withholding hits compensation no matter how much you earn, and the rate increases to 2.35% at higher compensation levels thanks to the 0.9% additional Medicare tax.
An S corporation employer makes matching payments except for the 0.9% Additional Medicare tax, which only falls on the employee. Therefore, the combined employee and employer FICA tax rate for the Social Security tax is 12.4%, and the combined rate for the Medicare tax is 2.9%, increasing to 3.8% at higher compensation levels — same as the corresponding SE tax rates.
Note: In this article, we’ll refer to the Social Security and Medicare taxes collectively as federal employment taxes whether paid as SE tax for self-employed folks or FICA tax for employees.
While wages paid to an S corporation shareholder-employee get hit with federal employment taxes, any remaining S corp taxable income that’s passed through to the employee-shareholder is exempt from federal employment taxes. The same is true for cash distributions paid out to a shareholder-employee. Since passed-through S corporation taxable income increases the tax basis of a shareholder-employee’s stock, distributions of corporate cash flow are usually free from federal income tax.
In appropriate circumstances, an S corp can follow the tax-saving strategy of paying modest, but justifiable, salaries to shareholder-employees. At the same time, it can pay out most or all of the remaining corporate cash flow in the form of federal-employment-tax-free shareholder distributions. In contrast, an owner’s share of net taxable income from a sole proprietorship, partnership and LLC (treated as a partnership for tax purposes) is generally subject to the full ravages of the SE tax.
Running your business as an S corporation and paying modest salaries to the shareholder-employee(s) may mean reduced capacity to make deductible contributions to tax-favored retirement accounts. For example, if an S corporation maintains a SEP, the maximum annual deductible contribution for a shareholder-employee is limited to 25% of salary. So the lower the salary, the lower the maximum contribution. However, if the S corp sets up a 401(k) plan, paying modest salaries generally won’t preclude generous contributions.
Converting an unincorporated business into an S corporation has other legal and tax implications. It’s a big decision. We can explain all the issues.
© 2023
Government officials saw a large increase in the number of new businesses launched during the COVID-19 pandemic. And the U.S. Census Bureau reports that business applications are still increasing slightly (up 0.4% from April 2023 to May 2023). The Bureau measures this by tracking the number of businesses applying for Employer Identification Numbers.
If you’re one of the entrepreneurs, you may not know that many of the expenses incurred by start-ups can’t be currently deducted on your tax return. You should be aware that the way you handle some of your initial expenses can make a large difference in your federal tax bill.
If you’re starting or planning to launch a new business, here are three rules to keep in mind:
In general, start-up expenses are those you incur to:
To qualify for the election, an expense also must be one that would be deductible if it were incurred after a business began. One example is money you spend analyzing potential markets for a new product or service.
To be eligible as an “organization expense,” an expense must be related to establishing a corporation or partnership. Some examples of organization expenses are legal and accounting fees for services related to organizing a new business and filing fees paid to the state of incorporation.
If you have start-up expenses that you’d like to deduct this year, you need to decide whether to take the election described above. Recordkeeping is critical. Contact us about your start-up plans. We can help with the tax and other aspects of your new business.
© 2023
As we increasingly embrace the post-pandemic era, the world of work has undergone a significant shift. Many companies have opted for remote work models, dispersing employees across various states and countries. However, while beneficial in many respects, this transition carries complex tax implications for businesses. Understanding and adapting these implications has become vital to business planning and decision-making.
To navigate the labyrinth of tax consequences linked with remote work, it’s crucial first to understand the term ‘nexus.’ In tax language, ‘nexus’ indicates a sufficient connection between a taxpayer and a jurisdiction that establishes tax obligations in that jurisdiction. Generally, there are two types of nexus tests – physical and economic.
One primary concern for remote workers and businesses is the potential risk of double taxation. Double taxation occurs when an employee works remotely in one state for a company located in another, resulting in tax obligations in both states. This can occur due to conflicting tax laws among states or the lack of coordination regarding the taxation rights of remote workers.
As such, the convenience of remote work might sometimes lead to the inconvenience of grappling with multiple state tax obligations. Understanding each state’s tax laws is essential and discussing with your financial advisor how to mitigate the risk of double taxation.
The location of your employees can impact your business’s tax obligations significantly. As a business owner, you may need to register with each state where you have employees and comply with all tax obligations, including corporate income tax, gross receipts tax, franchise tax, and sales and use tax.
In addition, employment tax requirements such as income tax withholding, unemployment insurance, and workers’ compensation insurance need to be addressed in each jurisdiction where a remote employee is located. Failure to comply with these obligations can result in penalties, affecting your business’s financial health.
Given the complexity of these tax issues, it’s important to conduct thorough research and consult with a financial advisor or tax professional. This can help you develop a comprehensive understanding of the relevant concepts, conduct regular reviews of the factors impacting your business, and, ultimately, avoid unwelcome surprises.
While navigating this new tax landscape can be challenging, it’s crucial to remember that being proactive in understanding these changes can help your business adapt more effectively to the evolving world of work. Through an informed approach and consistent monitoring, business owners can ensure compliance and take full advantage of the opportunities presented by the remote work model.
If you own or manage a business with employees, there’s a harsh tax penalty that you could be at risk for paying personally. The Trust Fund Recovery Penalty (TFRP) applies to Social Security and income taxes that are withheld by a business from its employees’ wages.
The TFRP is dangerous because it applies to a broad range of actions and to a wide range of people involved in a business.
Here are some answers to questions about the penalty:
What actions are penalized? The TFRP applies to any willful failure to collect, or truthfully account for, and pay over taxes required to be withheld from employees’ wages.
Why is it so harsh? Taxes are considered the government’s property. The IRS explains that Social Security and income taxes “are called trust fund taxes because you actually hold the employee’s money in trust until you make a federal tax deposit in that amount.”
The penalty is sometimes called the “100% penalty” because the person found liable is personally penalized 100% of the taxes due. The amounts the IRS seeks are usually substantial and the IRS is aggressive in enforcing the penalty.
Who’s at risk? The penalty can be imposed on anyone “responsible” for collecting and paying tax. This has been broadly defined to include a corporation’s officers, directors and shareholders, a partnership’s partners and any employee with related duties. In some circumstances, voluntary board members of tax-exempt organizations have been subject to this penalty. In other cases, responsibility has been extended to professional advisors and family members close to the business.
According to the IRS, responsibility is a matter of status, duty and authority. Anyone with the power to see that taxes are (or aren’t) paid may be responsible. There’s often more than one responsible person in a business, but each is at risk for the entire penalty. You may not be directly involved with the payroll tax withholding process in your business. But if you learn of a failure to pay withheld taxes and have the power to pay them, you become a responsible person. Although taxpayers held liable can sue other responsible people for contribution, this action must be taken entirely on their own after the TFRP is paid.
What’s considered willful? There doesn’t have to be an overt intent to evade taxes. Simply paying bills or obtaining supplies instead of paying over withheld taxes is willful behavior. And just because you delegate responsibilities to someone else doesn’t necessarily mean you’re off the hook. Failing to do the job yourself can be treated as willful.
Here are two cases that illustrate the risks.
Under no circumstances should you “borrow” from withheld amounts. All funds withheld should be paid over to the government on time. Contact us with any questions.
© 2023
As a small business owner, every decision you make can significantly impact your business’s financial health and profitability. Among your numerous choices, selecting the right accounting method for your business stands out for its importance. The accounting method you opt for shapes your business’s bookkeeping practices, affects your financial reporting, tax liabilities, and profitability, and influences your future decisions. This article aims to demystify the two primary accounting methods – cash and accrual accounting, helping you understand their implications and selecting the most appropriate one for your business’s needs.
At the core of accounting lie two main methods: cash-based and accrual-based accounting. Each approach has pros and cons and varies in suitability depending on your business’s size, scale, and nature.
Cash-Based Accounting: This method, characterized by simplicity and straightforwardness, records transactions only when cash is received or paid. It provides a clear picture of your actual cash flow, making it an ideal choice for small businesses, sole proprietors, or companies operating without inventory or on a purely cash basis. However, it’s worth noting that while this method helps you monitor your cash inflows and outflows closely, it might not offer a comprehensive overview of your financial health since it doesn’t account for outstanding receivables or payables.
Accrual-Based Accounting: Though more complex, this method provides a comprehensive picture of your financial status. Accrual-based accounting records income and expenses as earned or incurred, regardless of the actual cash transaction’s timing. It accounts for receivables, payables, assets, and liabilities, offering a real-time snapshot of your business’s financial status. This method benefits larger companies dealing with inventory, credit transactions, or businesses that are required to comply with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). However, it may seem overwhelming for small businesses due to its complexity and the resources required to maintain detailed records.
Deciding between cash-based and accrual-based accounting requires careful consideration of several key factors:
Remember, choosing an accounting method is not merely about understanding numbers; it’s about using this understanding to make informed decisions that align with your business’s financial goals. By selecting the right accounting method – cash or accrual – you can gain valuable insights into your business’s financial health and make decisions that steer your business toward a profitable future. The right choice will empower you, equipping you with the financial clarity necessary to successfully navigate your business’s financial landscape.
Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines affecting businesses and other employers during the third quarter of 2023. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. Contact us to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines and to learn more about the filing requirements.
July 31
August 10
September 15
© 2023
Your business may be able to claim big first-year depreciation tax deductions for eligible real estate expenditures rather than depreciate them over several years. But should you? It’s not as simple as it may seem.
For qualifying assets placed in service in tax years beginning in 2023, the maximum allowable first-year Section 179 depreciation deduction is $1.16 million. Importantly, the Sec. 179 deduction can be claimed for real estate qualified improvement property (QIP), up to the maximum annual allowance.
QIP includes any improvement to an interior portion of a nonresidential building that’s placed in service after the date the building is placed in service. For Sec. 179 deduction purposes, QIP also includes HVAC systems, nonresidential building roofs, fire protection and alarm systems and security systems that are placed in service after the building is first placed in service.
However, expenditures attributable to the enlargement of the building, any elevator or escalator, or the building’s internal structural framework don’t count as QIP and must be depreciated over several years.
A taxpayer’s Sec. 179 deduction can’t cause an overall business tax loss, and the maximum deduction is phased out if too much qualifying property is placed in service in the tax year. The Sec. 179 deduction limitation rules can get tricky if you own an interest in a pass-through business entity (partnership, LLC treated as a partnership for tax purposes, or S corporation). Finally, trusts and estates can’t claim Sec. 179 deductions, and noncorporate lessors face additional restrictions. We can give you full details.
Beyond the Sec. 179 deduction, 80% first-year bonus depreciation is also available for QIP that’s placed in service in calendar year 2023. If your objective is to maximize first-year write-offs, you’d claim the Sec. 179 deduction first. If you max out on that, then you’d claim 80% first-year bonus depreciation.
Note that for first-year bonus depreciation purposes, QIP doesn’t include nonresidential building roofs, HVAC systems, fire protection and alarm systems, or security systems.
Here are two reasons why you should think twice before claiming big first-year depreciation deductions for QIP.
First-year Sec. 179 deductions and bonus depreciation claimed for QIP can create depreciation recapture that’s taxed at higher ordinary income rates when the QIP is sold. Under current rules, the maximum individual rate on ordinary income is 37%, but you may also owe the 3.8% net investment income tax (NIIT).
On the other hand, for QIP held for more than one year, gain attributable to straight-line depreciation is taxed at an individual federal rate of only 25%, plus the 3.8% NIIT if applicable.
When you claim big first-year depreciation deductions for QIP, your depreciation deductions for future years are reduced accordingly. If federal income tax rates go up in future years, you’ll have effectively traded potentially more valuable future-year depreciation write-offs for less-valuable first-year write-offs.
As you can see, the decision to claim first-year depreciation deductions for QIP, or not claim them, can be complicated. Consult with us before making depreciation choices.
© 2023
If you and your employees are traveling for business this summer, there are a number of considerations to keep in mind. Under tax law, in order to claim deductions, you must meet certain requirements for out-of-town business travel within the United States. The rules apply if the business conducted reasonably requires an overnight stay.
Note: Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, employees can’t deduct their unreimbursed travel expenses on their own tax returns through 2025. That’s because unreimbursed employee business expenses are “miscellaneous itemized deductions” that aren’t deductible through 2025.
However, self-employed individuals can continue to deduct business expenses, including away-from-home travel expenses.
The actual costs of travel (for example, plane fare and cabs to the airport) are deductible for out-of-town business trips. You’re also allowed to deduct the cost of meals and lodging. Your meals are deductible even if they’re not connected to a business conversation or other business function. Although there was a temporary 100% deduction in 2021 and 2022 for business food and beverages provided by a restaurant, it was not extended to 2023. Therefore, there’s once again a 50% limit on deducting eligible business meals this year.
Keep in mind that no deduction is allowed for meal or lodging expenses that are “lavish or extravagant,” a term that’s been interpreted to mean “unreasonable.”
Personal entertainment costs on the trip aren’t deductible, but business-related costs such as those for dry cleaning, phone calls and computer rentals can be written off.
Some allocations may be required if the trip is a combined business/pleasure trip, for example, if you fly to a location for four days of business meetings and stay on for an additional three days of vacation. Only the costs of meals, lodging, etc., incurred for the business days are deductible — not those incurred for the personal vacation days.
On the other hand, with respect to the cost of the travel itself (plane fare, etc.), if the trip is primarily business, the travel cost can be deducted in its entirety and no allocation is required. Conversely, if the trip is primarily personal, none of the travel costs are deductible. An important factor in determining if the trip is primarily business or personal is the amount of time spent on each (although this isn’t the sole factor).
If the trip doesn’t involve the actual conduct of business but is for the purpose of attending a convention, seminar, etc., the IRS may check the nature of the meetings carefully to make sure it isn’t a vacation in disguise. Retain all material helpful in establishing the business or professional nature of this travel.
The rules for deducting the costs of a spouse who accompanies you on a business trip are very restrictive. No deduction is allowed unless the spouse is an employee of you or your company, and the spouse’s travel is also for a business purpose.
Finally, note that personal expenses you incur at home as a result of taking the trip aren’t deductible. For example, let’s say you have to board a pet while you’re away. The cost isn’t deductible. Contact us if you have questions about your small business deductions.
© 2023
When managing a business, KPIs can help provide insight into the business’s current health and past health. But what if you could use the data available to predict what KPIs will be in the future based on certain business decisions? With data science and machine learning, predictive analytics can be a reality for your business.
In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the amount of information available have grown exponentially, making integrating newer technologies into your business seem daunting or expensive, but it doesn’t have to be. AI uses data available to predict the outcomes of different business decisions on different levels. With the right models, AI can predict current customer preferences to help drive product development and forecast future demand.
As a CFO or business owner, you may find some hang-ups incorporating data science into your business strategy and reporting. With many other aspects of the business pulling your focus, you might find you’re continually attaching the label “later” to the project. Even if it’s not front of mind, it is an important task that could help you make better business decisions. In addition, the cost and time associated with implementing forward-thinking KPIs into strategy aren’t as expensive as you might think because jumping right in with a complete overhaul of your KPI dashboard and reporting programs is unnecessary. Getting started can be simplified by following the below steps.
While it may seem intuitive to give the data scientists and IT team cart blanche in implementing the AI programs, telling them to do what they do best, it’s essential to include the people who know your prospective client the best, as they are better versed in what questions to ask to get the answers they need to improve strategy. Look to your marketing, business development, and revenue teams to help guide this direction.
Implementing new predictive data science into your business strategy can be a massive, time-consuming task. Start by identifying the most critical KPIs and working with data to help move those numbers. Once you’ve identified your metrics, check if other businesses have tracked those metrics previously. There’s likely a framework you can follow instead of starting from scratch with data like transactional information, web analytics, and social media, saving you time.
Most marketing teams share similar challenges and goals when obtaining new clients. Focus on how your team measures ROI regarding acquisition, retention, and engagement and use that to generate future predictions. From there, analyze clients by predicting their lifetime value a few days after acquisition, then again at 7, 14, 30, and 180 days.
Once you have started to look at predictive insights to impact core KPIs, continue to look toward the future instead of falling back into habits of reviewing a snapshot of the past. Doing so will allow you to make decisions on which types of clients to focus on and where to invest your marketing and business development resources.
Embracing the recent advances in data science can help more efficiently direct your business’s time and resources to tasks that will improve your business’s performance.
If you’re claiming deductions for business meals or auto expenses, expect the IRS to closely review them. In some cases, taxpayers have incomplete documentation or try to create records months (or years) later. In doing so, they fail to meet the strict substantiation requirements set forth under tax law. Tax auditors are adept at rooting out inconsistencies, omissions and errors in taxpayers’ records, as illustrated by one recent U.S. Tax Court case.
In the case, a married couple claimed $13,596 in car and truck expenses, supported only by mileage logs that weren’t kept contemporaneously and were made using estimates rather than odometer readings. The court disallowed the entire deduction, stating that “subsequently prepared mileage records do not have the same high degree of credibility as those made at or near the time the vehicle was used and supported by documentary evidence.”
The court noted that it appeared the taxpayers attempted to deduct their commuting costs. However, it stated that “expenses a taxpayer incurs traveling between his or her home and place of business generally constitute commuting expenses, which … are nondeductible.”
A taxpayer isn’t relieved of the obligation to substantiate business mileage, even if he or she opts to use the standard mileage rate (65.5 cents per business mile in 2023), rather than keep track of actual expenses.
The court also ruled the couple wasn’t entitled to deduct $5,233 of travel, meal and entertainment expenses because they didn’t meet the strict substantiation requirements of the tax code. (TC Memo 2022-113)
This case is an example of why it’s critical to maintain meticulous records to support business expenses for vehicle and meal deductions. Here’s a list of “DOs and DON’Ts” to help meet the strict IRS and tax law substantiation requirements for these items:
DO keep detailed, accurate records. For each expense, record the amount, the time and place, the business purpose, and the business relationship of any person to whom you provided a meal. If you have employees who you reimburse for meals and auto expenses, make sure they’re complying with all the rules.
DON’T reconstruct expense logs at year end or wait until you receive a notice from the IRS. Take a moment to record the details in a log or diary or on a receipt at the time of the event or soon after. Require employees to submit monthly expense reports.
DO respect the fine line between personal and business expenses. Be careful about combining business and pleasure. Your business checking account shouldn’t be used for personal expenses.
DON’T be surprised if the IRS asks you to prove your deductions. Vehicle and meal expenses are a magnet for attention. Be prepared for a challenge.
With organization and guidance from us, your tax records can stand up to inspection from the IRS. There may be ways to substantiate your deductions that you haven’t thought of, and there may be a way to estimate certain deductions (called “the Cohan rule”), if your records are lost due to a fire, theft, flood or other disaster.
© 2023
As we approach the halfway point of 2023, it’s the perfect opportunity to evaluate your business tax planning and determine ways to decrease your tax burden. Employing the right strategies can reduce your taxes, optimize your cash flow, and enhance your long-term financial success.
In this article, we’ll introduce three tax strategies for 2023: Roth IRA conversions, tax loss harvesting, and year-round charitable giving. By familiarizing yourself with these tactics and how they can benefit your enterprise, you can make well-informed decisions and capitalize on available tax savings. Let’s dive into these tax-saving concepts and explore the options available for your business.
Roth IRA conversions effectively transform a portion of your traditional IRA into a tax-free asset that can provide you with cash distributions in your retirement years. Converting a portion of your traditional IRA can save you taxes at a potentially lower marginal tax rate and create a tax-free asset that can serve as a mechanism for tax redistribution during retirement. Even better, consider using this strategy as a future legacy asset for your beneficiaries.
By converting to a Roth IRA, you can ensure your desired assets are passed onto your loved ones.
Tax loss harvesting is a strategy that involves taking advantage of market volatility to generate a tax asset using captured capital losses. These losses can be used to offset future capital gains, and any remaining losses can be used to offset gains in subsequent years. Another effective strategy involves pairing these losses with qualified opportunity zones, which can further reduce your tax liabilities.
Investors who suffered losses due to the steep decline of the cryptocurrency and stock markets can benefit from this approach. The recent market downturn could also lead more investors to opportunity zone funds, presenting an excellent opportunity to maximize tax benefits.
End-of-year charitable donations have long been a go-to for taxpayers seeking tax deductions. However, there are benefits to giving year-round, especially when combined with investments.
For example, investors with appreciated securities in a taxable account can use these securities to fulfill their philanthropic goals. This strategy allows for a fair market value deduction without having to pay taxes on the capital gain. It’s a practical way to donate without sacrificing your end-of-the-year cash or check donation.
Charitable remainder trusts offer another means of donating to worthwhile causes and taking advantage of tax breaks. Although the lower interest rates over the last few years have cooled investor interest in these trusts, the benefits of using these trusts become increasingly clear as rates rise.
Don’t wait until the end of the year to give back. Consider these charitable giving strategies to boost your philanthropic impact and build a better future.
Remember, it’s essential to review your tax planning regularly to take advantage of available opportunities and ensure you’re putting your assets to their best use. With these actionable takeaways, you can start making informed decisions today and set your business up for long-term financial success.
The IRS recently released guidance providing the 2024 inflation-adjusted amounts for Health Savings Accounts (HSAs).
An HSA is a trust created or organized exclusively for the purpose of paying the “qualified medical expenses” of an “account beneficiary.” An HSA can only be established for the benefit of an “eligible individual” who is covered under a “high-deductible health plan.” In addition, a participant can’t be enrolled in Medicare or have other health coverage (exceptions include dental, vision, long-term care, accident and specific disease insurance).
Within specified dollar limits, an above-the-line tax deduction is allowed for an individual’s contributions to an HSA. This annual contribution limitation and the annual deductible and out-of-pocket expenses under the tax code are adjusted annually for inflation.
In Revenue Procedure 2023-23, the IRS released the 2024 inflation-adjusted figures for contributions to HSAs, which are as follows:
Annual contribution limitation. For calendar year 2024, the annual contribution limitation for an individual with self-only coverage under an HDHP will be $4,150. For an individual with family coverage, the amount will be $8,300. This is up from $3,850 and $7,750, respectively, in 2023.
There is an additional $1,000 “catch-up” contribution amount for those age 55 and older in 2024 (and 2023).
High-deductible health plan defined. For calendar year 2024, an HDHP will be a health plan with an annual deductible that isn’t less than $1,600 for self-only coverage or $3,200 for family coverage (up from $1,500 and $3,000, respectively, in 2023). In addition, annual out-of-pocket expenses (deductibles, co-payments, and other amounts, but not premiums) won’t be able to exceed $8,050 for self-only coverage or $16,100 for family coverage (up from $7,500 and $15,000, respectively, in 2023).
There are a variety of benefits to HSAs. Contributions to the accounts are made on a pre-tax basis. The money can accumulate tax-free year after year and can be withdrawn tax-free to pay for a variety of medical expenses such as doctor visits, prescriptions, chiropractic care and premiums for long-term care insurance. In addition, an HSA is “portable.” It stays with an account holder if he or she changes employers or leaves the workforce. Contact your employee benefits and tax advisors if you have questions about HSAs at your business.
© 2023
Many businesses use independent contractors to help keep their costs down — especially in these times of staff shortages and inflationary pressures. If you’re among them, be careful that these workers are properly classified for federal tax purposes. If the IRS reclassifies them as employees, it can be an expensive mistake.
The question of whether a worker is an independent contractor or an employee for federal income and employment tax purposes is a complex one. If a worker is an employee, your company must withhold federal income and payroll taxes and pay the employer’s share of FICA taxes on the wages, plus FUTA tax. A business may also provide the worker with fringe benefits if it makes them available to other employees. In addition, there may be state tax obligations.
On the other hand, if a worker is an independent contractor, these obligations don’t apply. In that case, the business simply sends the contractor a Form 1099-NEC for the year showing the amount paid (if it’s $600 or more).
Who’s an “employee?” Unfortunately, there’s no uniform definition of the term.
The IRS and courts have generally ruled that individuals are employees if the organization they work for has the right to control and direct them in the jobs they’re performing. Otherwise, the individuals are generally independent contractors. But other factors are also taken into account including who provides tools and who pays expenses.
Some employers that have misclassified workers as independent contractors may get some relief from employment tax liabilities under Section 530. This protection generally applies only if an employer meets certain requirements. For example, the employer must file all federal returns consistent with its treatment of a worker as a contractor and it must treat all similarly situated workers as contractors.
Note: Section 530 doesn’t apply to certain types of workers.
Be aware that you can ask the IRS (on Form SS-8) to rule on whether a worker is an independent contractor or employee. However, you should also be aware that the IRS has a history of classifying workers as employees rather than independent contractors.
Businesses should consult with us before filing Form SS-8 because it may alert the IRS that your business has worker classification issues — and it may unintentionally trigger an employment tax audit.
It may be better to properly set up a relationship with workers to treat them as independent contractors so that your business complies with the tax rules.
Workers who want an official determination of their status can also file Form SS-8. Dissatisfied independent contractors may do so because they feel entitled to employee benefits and want to eliminate their self-employment tax liabilities.
If a worker files Form SS-8, the IRS will notify the business with a letter. It identifies the worker and includes a blank Form SS-8. The business is asked to complete and return the form to the IRS, which will render a classification decision.
These are the basic tax rules. Contact us if you’d like to discuss how to classify workers at your business. We can help make sure that your workers are properly classified.
© 2023
Whether you’re operating a new company or an established business, losses can happen. The federal tax code may help soften the blow by allowing businesses to apply losses to offset taxable income in future years, subject to certain limitations.
The net operating loss (NOL) deduction addresses the tax inequities that can exist between businesses with stable income and those with fluctuating income. It essentially lets the latter average out their income and losses over the years and pay tax accordingly.
You may be eligible for the NOL deduction if your deductions for the tax year are greater than your income. The loss generally must be caused by deductions related to your:
The following generally aren’t allowed when determining your NOL:
Individuals and C corporations are eligible to claim the NOL deduction. Partnerships and S corporations generally aren’t eligible, but partners and shareholders can use their separate shares of the business’s income and deductions to calculate individual NOLs.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) made significant changes to the NOL rules. Previously, taxpayers could carry back NOLs for two years, and carry forward the losses 20 years. They also could apply NOLs against 100% of their taxable income.
The TCJA limits the NOL deduction to 80% of taxable income for the year and eliminates the carryback of NOLs (except for certain farming losses). However, it does allow NOLs to be carried forward indefinitely.
A COVID-19 relief law temporarily loosened the TCJA restrictions. It allowed NOLs arising in 2018, 2019 or 2020 to be carried back five years and removed the taxable income limitation for years beginning before 2021. As a result, NOLs could completely offset income. However, these provisions have expired.
If your NOL carryforward is more than your taxable income for the year to which you carry it, you may have an NOL carryover. The carryover will be the excess of the NOL deduction over your modified taxable income for the carryforward year. If your NOL deduction includes multiple NOLs, you must apply them against your modified taxable income in the same order you incurred them, beginning with the earliest.
The TCJA established an “excess business loss” limitation, which took effect in 2021. For partnerships or S corporations, this limitation is applied at the partner or shareholder level, after the outside basis, at-risk and passive activity loss limitations have been applied.
Under the rule, noncorporate taxpayers’ business losses can offset only business-related income or gain, plus an inflation-adjusted threshold. For 2023, that threshold is $289,000 ($578,000 if married filing jointly). Remaining losses are treated as an NOL carryforward to the next tax year. In other words, you can’t fully deduct them because they become subject to the 80% income limitation on NOLs, reducing their tax value.
Important: Under the Inflation Reduction Act, the excess business loss limitation applies to tax years beginning before January 1, 2029. Under the TCJA, it had been scheduled to expire after December 31, 2026.
The tax rules regarding business losses are complex, especially when accounting for how NOLs can interact with other potential tax breaks. We can help you chart the best course forward.
© 2023
As a business owner, you understand the importance of making the right decisions and keeping your finances to survive. When you want to thrive, however, you need the kind of insight and experience that will drive strategy and deliver results. The sharp financial perspective of a CFO can make a world of difference in a company’s success, but hiring one isn’t always feasible or affordable. Enter the Chief Financial Officer consultant. A CFO consultant can assess your financial situation, market nuances, and industry outlook to bring the big picture into focus. Keep reading to learn how the perspective of a CFO can benefit your business.
While you may think of a CFO as another accountant or finance-focused person, the reality is much more complex. The best CFOs are responsible for many essential business tasks and decisions, which business owners may need more time or knowledge to focus on. The role of the CFO means looking at the past to find the best ways to drive the present into the future the organization wants. They work with budgets, forecasts, vendor relationships, tax strategy, compliance, succession planning, and more to guide other leaders toward a unified goal.
When you bring a CFO on full-time, they look for ways to save costs and drive additional financial growth for the organization. Some of the ways they do this are by working with the following:
Working with an outsourced Chief Financial Officer provides a level of expertise based on experience with other clients who are either within your industry or have been through similar situations. This experience allows them to provide scalable knowledge and assistance without the hours of research a business owner or manager may have to complete for the same results. The CFO is focused on the larger picture and understands which details will make a difference in the future of the business.
The cost of bringing on a full-time CFO is unrealistic for many businesses, but that doesn’t mean they need to go without a CFO perspective. CFO consultants, or outsourced CFOs, provide the value of a CFO without being cost-prohibitive. Many businesses that work with an outsourced CFO experience cost-savings or revenue growth that either makes up for or outpaces the outlay for the consulting service.
Whether you’ve hit a wall or feel like your business could be doing so much more, there are many reasons to seek an outsider’s perspective. Don’t leave this critical task to just anyone; work with someone who has experience directing businesses through important decisions. They can help you face strategic challenges, deliberate on new avenues of growth, or convert decisions into action.
If you’re ready to bring in the expertise of a CFO, contact our professionals here.
If you’re the owner of an incorporated business, you know there’s a tax advantage to taking money out of a C corporation as compensation rather than as dividends. The reason: A corporation can deduct the salaries and bonuses that it pays executives, but not dividend payments. Therefore, if funds are paid as dividends, they’re taxed twice, once to the corporation and once to the recipient. Money paid out as compensation is only taxed once — to the employee who receives it.
However, there are limits to how much money you can take out of the corporation this way. Under tax law, compensation can be deducted only to the extent that it’s reasonable. Any unreasonable portion isn’t deductible and, if paid to a shareholder, may be taxed as if it were a dividend. Keep in mind that the IRS is generally more interested in unreasonable compensation payments made to someone “related” to a corporation, such as a shareholder-employee or a member of a shareholder’s family.
There’s no simple way to determine what’s reasonable. If the IRS audits your tax return, it will examine the amount that similar companies would pay for comparable services under similar circumstances. Factors that are taken into account include the employee’s duties and the amount of time spent on those duties, as well as the employee’s skills, expertise and compensation history. Other factors that may be reviewed are the complexities of the business and its gross and net income.
There are four steps you can take to make it more likely that the compensation you earn will be considered “reasonable,” and therefore deductible by your corporation:
You can avoid problems and challenges by planning ahead. Contact us if you have questions or concerns about your situation.
© 2023
Fraud. Scam. Phishing. Regardless of what you call these illicit activities, it’s important to protect yourself against the bad players that take advantage of weaknesses for their gain. Not only is it inconvenient, but there’s often a financial cost when you’re a victim of fraud.
The IRS releases an annual ‘Dirty Dozen’ list featuring the top taxpayer scams for the coming year. The list is certainly not exhaustive of every potential pitfall out there, but it is an excellent place to start educating yourself (and your team if you’re a business owner). Here’s a summary of the 2023 IRS Dirty Dozen.
Employer Retention Credit Promoters: Businesses have been targeted by companies claiming to help them submit tax returns and adjustments to take maximum advantage of the Employee Retention Credit (ERC). These promoters collect a fee for preparation services, which is often tied to the value of the proposed credit. Usually, the targeted businesses don’t qualify for the credit, so when the adjustment claim is either rejected by the IRS or found to be incorrect during an audit, the business is out the funds paid to the promoter, as well as any monies received from the ERC they were not eligible for and potential IRS fees.
Phishing and Smishing Scams: Emails, texts, phone calls. These are all popular channels for scammers trying to obtain sensitive information from taxpayers by lying and saying they work for the IRS. Please remember that the IRS will always initiate contact with taxpayers by mail.
Online Account Assistance: The IRS Online Account tool provides helpful information to taxpayers. Scammers are using this as an opportunity to learn social security numbers and other sensitive information by calling and offering to help taxpayer set up their online accounts. This can lead to identity theft and a big headache for taxpayers trying to sort everything out.
Fuel Tax Credit Promoters: Like the Employee Retention Credit promotors, Fuel Tax Credit promoters claim that the taxpayer is qualified for the credit when they may not be. These scammers usually charge a big fee to assist the taxpayer in submitting these claims.
Fake Charity Scams: Major disasters like hurricanes, floods, and wildfires can lead to an increase in counterfeit charities to dupe taxpayers. When these disasters occur, people want to help those affected. Scammers take advantage of this generosity by using fake charities as a front for stealing money and private information. Be sure to take the time to thoroughly research any organization before donating.
Shady Tax Preparers: Common warning signs of a shady tax preparer include charging a fee based on the size of the refund or refusing to sign the form as a preparer as required by law. Make sure you’re using a trusted and knowledgeable tax preparer.
Social Media Trends: While this may seem unsurprising to most, it bears repeating – you can’t always trust what you hear on the internet. Social media can circulate misinformation quickly, including ‘hacks’ for getting a bigger tax refund. These trends usually involve lying on tax forms or creating false income. The IRS reminds taxpayers that falsifying tax documents is illegal and penalties are involved.
Spearphishing Email Scams: Bad players have been sending email requests to tax preparers, and payroll and human resources teams to try and gain sensitive client and employee data like W-2 information. These requests can look like they’re from a potential new client, and the scammers then use the data they collect to submit a series of false tax refund filings and collect on the tax returns. Businesses can protect themselves with these cybersecurity tips.
Offer in Compromise Mills: Promoters target taxpayers that owe the IRS money by offering to settle their debts with the IRS at a steep discount for a fee. Many times, the targeted taxpayers don’t meet the technical requirements to obtain an offer, meaning they still owe the IRS the same amount and are paying excessive fees to these companies. Taxpayers can check their eligibility for an Offer in Compromise using this free IRS tool.
Charitable Remainder Annuity Trust Schemes: Promoters can misuse Charitable Remainder Annuity Trusts and monetized installment sales by misapplying the rules, leaving filers vulnerable. These types of schemes are often targeted at wealthy taxpayers.
Tax Avoidance Schemes: The IRS warns taxpayers to be wary of anyone claiming to reduce their taxes owed drastically or even to nothing. This could include micro-captive insurance arrangements, international accounts, and syndicated conservation easements.
Be diligent with your information, teach your employees how to recognize scams, and be sure to discuss any changes in tax strategy with your trusted tax professional. If anyone contacts you with a claim that seems too good to be true, it probably is.
If your business occupies substantial space and needs to increase or move from that space in the future, you should keep the rehabilitation tax credit in mind. This is especially true if you favor historic buildings.
The credit is equal to 20% of the qualified rehabilitation expenditures (QREs) for a qualified rehabilitated building that’s also a certified historic structure. A qualified rehabilitated building is a depreciable building that has been placed in service before the beginning of the rehabilitation and is used, after rehabilitation, in business or for the production of income (and not held primarily for sale). Additionally, the building must be “substantially” rehabilitated, which generally requires that the QREs for the rehabilitation exceed the greater of $5,000 or the adjusted basis of the existing building.
A QRE is any amount chargeable to capital and incurred in connection with the rehabilitation (including reconstruction) of a qualified rehabilitated building. QREs must be for real property (but not land) and can’t include building enlargement or acquisition costs.
The 20% credit is allocated ratably to each year in the five-year period beginning in the tax year in which the qualified rehabilitated building is placed in service. Thus, the credit allowed in each year of the five-year period is 4% (20% divided by 5) of the QREs with respect to the building. The credit is allowed against both regular federal income tax and alternative minimum tax.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which was signed at the end of 2017, made some changes to the credit. Specifically, the law:
Contact us to discuss the technical aspects of the rehabilitation credit. There may also be other federal tax benefits available for the space you’re contemplating. For example, various tax benefits might be available depending on your preferences as to how a building’s energy needs will be met and where the building is located. In addition, there may be state or local tax and non-tax subsidies available.
Getting beyond these preliminary considerations, we can work with you and construction professionals to determine whether a specific available “old” building can be the subject of a rehabilitation that’s both tax-credit-compliant and practical to use. And, if you do find a building that you decide you’ll buy (or lease) and rehabilitate, we can help you monitor project costs and substantiate the compliance of the project with the requirements of the credit and any other tax benefits.
© 2023
California taxpayers should note the changes made to these tax laws over the last several months. Here’s an overview of what you may have missed:
California law requires holders of unclaimed property to attempt to notify owners of the property regularly, to keep records of the property and to turn over the property to the State Controller’s Office after the appropriate dormancy period. Unclaimed property could be:
Under California Assembly Bill 466, the dormancy period has been set to one year for payroll accounts and three years for Securities, Accounts Receivable and Payable, and Disbursements. The law also requires businesses to review their books and records annually to determine if they have any unclaimed property to report. Keep in mind, businesses must also complete the following reporting requirements:
In addition, the State of California identifies the following filling and reporting deadlines:
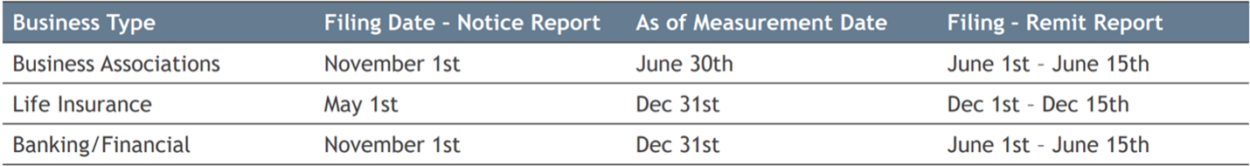
Personal property owners in California will receive annual assessments and tax bills for the personal property based on their county or local jurisdiction laws. In order to stay in compliance with tax laws, keep these points in mind:
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act limited the state tax deduction for personal income in pass-through entities to $10,000. In California, pass-through entities pay tax, and the PTE owns remain taxable on the distributive shares of income. However, the owners receive a tax credit for a share of the PTE tax. The nonrefundable tax credit can be carried forward for up to 5 years.
In order to qualify as a pass-through entity, the election must be made annually and consented to by each owner to the pass-through entity. Payments of more than $1,000 or 50% of the prior year PTE tax are due by June 15 of the current tax year, with the remaining due on March 15 of the following year. This is effective for tax years beginning January 1, 2021 or later and before January 1, 2026.
The following are business taxes that business owners should be aware of for San Francisco and Los Angeles.
In late 2022 and early 2023, California issued qualified taxpayers a total of $9.2 billion in refunds of tax overpayments, called the Middle Class Tax Refund. The State of California noted these payments are not liable for state taxes previously. In February, the IRS determined that it will not challenge the tax treatment of these payments on 2022 tax filings, citing their general welfare and disaster relief exception.
Due to historically high rain, snow, and flooding in much of California, the IRS is offering disaster relief assistance in the form of due date extensions on required tax filings and payments. The new deadline for tax payments due from January through October is October 16, 2023. This includes:
For more information on the counties qualified for tax relief and what payments have been extended, please visit the IRS press release or call our team.
If you’re thinking about setting up a retirement plan for yourself and your employees, but you’re worried about the financial commitment and administrative burdens involved, there are a couple of options to consider. Let’s take a look at a “simplified employee pension” (SEP) or a “savings incentive match plan for employees” (SIMPLE).
SEPs are intended as an attractive alternative to “qualified” retirement plans, particularly for small businesses. The features that are appealing include the relative ease of administration and the discretion that you, as the employer, are permitted in deciding whether or not to make annual contributions.
If you don’t already have a qualified retirement plan, you can set up a SEP simply by using the IRS model SEP, Form 5305-SEP. By adopting and implementing this model SEP, which doesn’t have to be filed with the IRS, you’ll have satisfied the SEP requirements. This means that as the employer, you’ll get a current income tax deduction for contributions you make on behalf of your employees. Your employees won’t be taxed when the contributions are made but will be taxed later when distributions are made, usually at retirement. Depending on your needs, an individually-designed SEP — instead of the model SEP — may be appropriate for you.
When you set up a SEP for yourself and your employees, you’ll make deductible contributions to each employee’s IRA, called a SEP-IRA, which must be IRS-approved. The maximum amount of deductible contributions that you can make to an employee’s SEP-IRA, and that he or she can exclude from income, is the lesser of: 25% of compensation and $66,000 for 2023. The deduction for your contributions to employees’ SEP-IRAs isn’t limited by the deduction ceiling applicable to an individual’s own contribution to a regular IRA. Your employees control their individual IRAs and IRA investments, the earnings on which are tax-free.
There are other requirements you’ll have to meet to be eligible to set up a SEP. Essentially, all regular employees must elect to participate in the program, and contributions can’t discriminate in favor of the highly compensated employees. But these requirements are minor compared to the bookkeeping and other administrative burdens connected with traditional qualified pension and profit-sharing plans.
The detailed records that traditional plans must maintain to comply with the complex nondiscrimination regulations aren’t required for SEPs. And employers aren’t required to file annual reports with IRS, which, for a pension plan, could require the services of an actuary. The required recordkeeping can be done by a trustee of the SEP-IRAs — usually a bank or mutual fund.
Another option for a business with 100 or fewer employees is a “savings incentive match plan for employees” (SIMPLE). Under these plans, a “SIMPLE IRA” is established for each eligible employee, with the employer making matching contributions based on contributions elected by participating employees under a qualified salary reduction arrangement. The SIMPLE plan is also subject to much less stringent requirements than traditional qualified retirement plans. Or, an employer can adopt a “simple” 401(k) plan, with similar features to a SIMPLE plan, and automatic passage of the otherwise complex nondiscrimination test for 401(k) plans.
For 2023, SIMPLE deferrals are up to $15,500 plus an additional $3,500 catch-up contributions for employees ages 50 and older.
Contact us for more information or to discuss any other aspect of your retirement planning.
© 2023
Summer is around the corner so you may be thinking about hiring young people at your small business. At the same time, you may have children looking to earn extra spending money. You can save family income and payroll taxes by putting your child on the payroll. It’s a win-win!
Here are four tax advantages.
You can turn some of your high-taxed income into tax-free or low-taxed income by shifting some business earnings to a child as wages for services performed. In order for your business to deduct the wages as a business expense, the work done by the child must be legitimate and the child’s salary must be reasonable.
For example, suppose you’re a sole proprietor in the 37% tax bracket. You hire your 16-year-old son to help with office work full-time in the summer and part-time in the fall. He earns $10,000 during the year (and doesn’t have other earnings). You can save $3,700 (37% of $10,000) in income taxes at no tax cost to your son, who can use his $13,850 standard deduction for 2023 to shelter his earnings.
Family taxes are cut even if your son’s earnings exceed his standard deduction. That’s because the unsheltered earnings will be taxed to him beginning at a 10% rate, instead of being taxed at your higher rate.
Your business likely will have to withhold federal income taxes on your child’s wages. Usually, an employee can claim exempt status if he or she had no federal income tax liability for last year and expects to have none this year.
However, exemption from withholding can’t be claimed if: 1) the employee’s income exceeds $1,250 for 2023 (and includes more than $400 of unearned income), and 2) the employee can be claimed as a dependent on someone else’s return.
Keep in mind that your child probably will get a refund for part or all of the withheld tax when filing a return for the year.
If your business isn’t incorporated, you can also save some Social Security tax by shifting some of your earnings to your child. That’s because services performed by a child under age 18 while employed by a parent aren’t considered employment for FICA tax purposes.
A similar but more liberal exemption applies for FUTA (unemployment) tax, which exempts earnings paid to a child under age 21 employed by a parent. The FICA and FUTA exemptions also apply if a child is employed by a partnership consisting only of his or her parents.
Note: There’s no FICA or FUTA exemption for employing a child if your business is incorporated or is a partnership that includes non-parent partners. However, there’s no extra cost to your business if you’re paying a child for work you’d pay someone else to do.
Your business also may be able to provide your child with retirement savings, depending on your plan and how it defines qualifying employees. For example, if you have a SEP plan, a contribution can be made for the child up to 25% of his or her earnings (not to exceed $66,000 for 2023).
Contact us if you have any questions about these rules in your situation. Keep in mind that some of the rules about employing children may change from year to year and may require your income-shifting strategies to change too.
© 2023
If you’re starting a business with some partners and wondering what type of entity to form, an S corporation may be the most suitable form of business for your new venture. Here are some of the reasons why.
A big benefit of an S corporation over a partnership is that as S corporation shareholders, you won’t be personally liable for corporate debts. In order to receive this protection, it’s important that:
If you expect that the business will incur losses in its early years, an S corporation is preferable to a C corporation from a tax standpoint. Shareholders in a C corporation generally get no tax benefit from such losses. In contrast, as S corporation shareholders, each of you can deduct your percentage share of losses on your personal tax return to the extent of your basis in the stock and in any loans you made to the entity. Losses that can’t be deducted because they exceed your basis are carried forward and can be deducted by you in the future when there’s sufficient basis.
Once the S corporation begins to earn profits, the income will be taxed directly to you whether or not it’s distributed. It will be reported on your individual tax return and be aggregated with income from other sources. Your share of the S corporation’s income won’t be subject to self-employment tax, but your wages will be subject to Social Security taxes. To the extent the income is passed through to you as qualified business income (QBI), you’ll be eligible to take the 20% pass-through deduction, subject to various limitations.
Note: Unless Congress acts to extend it, the QBI deduction is scheduled to expire after 2025.
If you’re planning to provide fringe benefits such as health and life insurance, you should be aware that the costs of providing such benefits to a more than 2% shareholder are deductible by the entity but are taxable to the recipient.
Also, be aware that the S corporation could inadvertently lose its S status if you or your partners transfer stock to an ineligible shareholder, such as another corporation, a partnership, or a nonresident alien. If the S election was terminated, the corporation would become a taxable entity. You would not be able to deduct any losses, and earnings could be subject to double taxation — once at the corporate level and again when distributed to you. In order to protect against this risk, it’s a good idea for each shareholder to sign an agreement promising not to make any transfers that would jeopardize the S election.
Before finalizing your choice of entity, consult with us. We can answer any questions you have and assist in launching your new venture.
© 2023
The new lease accounting methods have been an important topic for businesses over the last few years. Determining if an enforceable lease exists is an integral part of Topic 842 that affects how and what gets reported under these lease accounting methods. Compliance for certain leases is being simplified for organizations that fall under common control arrangements, such as parent organizations and subsidiaries. The Financial Accounting Standards Board voted to enact the following changes when the update to Topic 842 is released.
The FASB has voted to adopt the proposed November update as written for nonprofit organizations and private entities under common control. This update would simplify the compliance approach for these organizations by allowing them to use written terms and conditions to help determine if an enforceable lease arrangement is in place. This workaround is expected to be welcomed by smaller organizations, as the complex analysis for lease agreements can be costly and take time.
The FASB allows this method under their ‘practical expedient’ policy. However, please note practical expedience cannot be used in the absence of written terms and conditions.
For properties under a common control lease, changes to the current standards are being made to account for improvements made to the property. Under the new rule, the cost of improvements should amortize over the ‘useful life’ of the improvements. This should be scheduled out regardless of lease terms if the common control lease group uses the property throughout the lease. Previously, improvements could only be amortized over the terms of the lease. This change applies to public, private, and nonprofit organizations.
Moving forward, you may need to change how your organization handles leases in common control groups. Do not act on these changes until the FASB formally releases the update, which is expected by the end of March 2023.
Lease accounting standards can be complex and confusing. For guidance on setting up your firm’s lease accounting system or auditing the current system in place, please get in touch with our knowledgeable team members today.
Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines that apply to businesses and other employers during the second quarter of 2023. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. Contact us to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines and to learn more about the filing requirements.
© 2023
In our rapidly evolving information era, new rules and regulations pressure businesses to consolidate their financial reporting process. But depending on your financial system, running these reports can require extensive manual work, exposing your reporting to user errors. While many businesses have turned to enterprise resource planning (ERP) automation, a recent article claims less than half of companies’ automation initiatives are currently meeting their objectives. Combine these factors with a lack of workflow coordination, data inconsistencies, and feeble post-close review, and you have a recipe for disaster.
Organizations and CFOs often encounter problems with data quality management, missing skills and resources, support of the executive suite, and a lack of clear processes. If your company is spending more and more time on the financial close process, it is probably time to upgrade to a more agile approach. Start with these steps to improve your financial close process and streamline reporting.
Is your organization fully utilizing the features available in your current financial system? Evaluate software utilization, potential overlap, areas of overcomplexity, and poor standardization processes. A thorough review of your current system’s capabilities will help you understand what’s possible and introduce efficiencies to your organization.
The primary purpose of an enterprise resource planning (ERP) or financial management system is to provide a central database of all system applications. Robust database systems are key to modern finance departments but aren’t always ready to scale. Companies can fill the gaps in their current system with add-on point solutions or robotic process automation (RPA) but should be aware of cost, maintenance, and security implications. Plugging the gap will likely require a more strategic approach. Our professionals can help you orchestrate and implement process transformation that works with your systems and your business.
Poor-quality data can act as a stopgap. Make the time to understand the purpose of the data used in the business, where the numbers come from, and their relationships with other metrics. To reduce these speed bumps along the way:
Change is well and good, but progress will stall if you don’t have the support of the executive team or the people who will be implementing the change. Make certain the proposed changes align with the organization’s strategy. Then, align the people to the processes and each other. Organizations need to be able to pivot quickly. With buy-in from the correct individuals, you can shift your organization toward the future when regulatory updates arise or gaps are exposed.
Use these steps to build a technological infrastructure that allows for change and drives data efficiency. If you need recommendations on streamlining your financial reporting processes, contact our team of advisors today!
It’s been years since the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) of 2017 was signed into law, but it’s still having an impact. Several provisions in the law have expired or will expire in the next few years. One provision that took effect last year was the end of current deductibility for research and experimental (R&E) expenses.
The TCJA has affected many businesses, including manufacturers, that have significant R&E costs. Starting in 2022, Internal Revenue Code Section 174 R&E expenditures must be capitalized and amortized over five years (15 years for research conducted outside the United States). Previously, businesses had the option of deducting these costs immediately as current expenses.
The TCJA also expanded the types of activities that are considered R&E for purposes of IRC Sec. 174. For example, software development costs are now considered R&E expenses subject to the amortization requirement.
Businesses should consider the following strategies for minimizing the impact of these changes:
For 2022 tax returns, the IRS recently released guidance for taxpayers to change the treatment of R&E expenses (Revenue Procedure 2023-11). The guidance provides a way to obtain automatic consent under the tax code to change methods of accounting for specified research or experimental expenditures under Sec. 174, as amended by the TCJA. This is important because unless there’s an exception provided under tax law, a taxpayer must secure the consent of the IRS before changing a method of accounting for federal income tax purposes.
The recent revenue procedure also provides a transition rule for taxpayers who filed a tax return on or before January 17, 2023.
We can advise you how to proceed. There have also been proposals in Congress that would eliminate the amortization requirements. However, so far, they’ve been unsuccessful. We’re monitoring legislative developments and can help adjust your tax strategies if there’s a change in the law.
© 2023
Under tax law, businesses can generally deduct advertising and marketing expenses that help keep existing customers and bring in new ones. This valuable tax deduction can help businesses cut their taxes.
However, in order to be deductible, advertising and marketing expenses must be “ordinary and necessary.” As one taxpayer recently learned in U.S. Tax Court, not all expenses are eligible. An ordinary expense is one that’s common and accepted in the industry. And a necessary expense is one that’s helpful and appropriate for the business.
According to the IRS, here are some advertising expenses that are usually deductible:
An attorney deducted his car-racing expenses and claimed they were advertising for his personal injury law practice. He contended that his racing expenses, totaling over $303,000 for six tax years, were deductible as advertising because the car he raced was sponsored by his law firm.
The IRS denied the deductions and argued that the attorney’s car racing wasn’t an ordinary and necessary expense paid or incurred while carrying on his business of practicing law. The Tax Court agreed with the IRS.
When making an ordinary and necessary determination for an expense, most courts look to the taxpayer’s primary motive for incurring the expense and whether there’s a “proximate” relationship between the expense and the taxpayer’s occupation. In this case, the taxpayer’s car-racing expenses were neither necessary nor common for a law practice, so there was no “proximate” relationship between the expense and the taxpayer’s occupation. And, while the taxpayer said his primary motive for incurring the expense was to advertise his law business, he never raced in the state where his primary law practice was located, and he never actually got any legal business from his car-racing activity.
The court noted that the car “sat in his garage” after he returned to the area where his law practice was located. The court added that even if the taxpayer raced in that area, “we would not find his expenses to be legitimate advertising expenses. His name and a decal for his law firm appeared in relatively small print” on his car.
This form of “signage,” the court stated, “is at the opposite end of the spectrum from (say) a billboard or a newspaper ad. Indeed, every driver’s name typically appeared on his or her racing car.” (TC Memo 2023-18)
There are no deductions allowed for personal expenses or hobbies. But as explained above, you can deduct ordinary and necessary advertising and marketing expenses in a bona fide business. The key to protecting your deductions is to keep meticulous records to substantiate them. Contact us with questions about your situation.
© 2023
If you’re buying or replacing a vehicle that you’ll use in your business, be aware that a heavy SUV may provide a more generous tax break this year than you’d get from a smaller vehicle. The reason has to do with how smaller business cars are depreciated for tax purposes.
Business cars are subject to more restrictive tax depreciation rules than those that apply to other depreciable assets. Under the so-called “luxury auto” rules, depreciation deductions are artificially “capped.” Those caps also extend to the alternative deduction that a taxpayer can claim if it elects to use Section 179 expensing for all or part of the cost of a business car. (It allows you to write-off an asset in the year it’s placed in service.)
These rules include smaller trucks or vans built on truck chassis that are treated as cars. For most cars that are subject to the caps and that are first placed in service in calendar year 2023, the maximum depreciation and/or expensing deductions are:
Generally, the effect is to extend the number of years it takes to fully depreciate the vehicle.
Because of the restrictions for cars, you may be better off from a tax timing perspective if you replace your business car with a heavy SUV instead of another car. That’s because the caps on annual depreciation and expensing deductions for passenger automobiles don’t apply to trucks or vans that are rated at more than 6,000 pounds gross (loaded) vehicle weight. This includes large SUVs, many of which are priced over $50,000.
The result is that in most cases, you’ll be able to write-off a majority of the cost of a new SUV used entirely for business purposes by utilizing bonus and regular depreciation in the year you place it into service. For 2023, bonus depreciation is available at 80%, but is being phased down to zero over the next few years.
If you consider electing Section 179 expensing for all or part of the cost of an SUV, you need to know that an inflation-adjusted limit, separate from the general caps described above, applies ($28,900 for an SUV placed in service in tax years beginning in 2023, up from $27,000 for an SUV placed in service in tax years beginning in 2022). There’s also an aggregate dollar limit for all assets elected to be expensed in the year that would apply. Following the expensing election, you would then depreciate the remainder of the cost under the usual rules without regard to general annual caps.
Please note that the tax benefits described above are all subject to adjustment for non-business use. Also, if business use of an SUV doesn’t exceed 50% of total use, the SUV won’t be eligible for the expensing election, and would have to be depreciated on a straight-line method over a six-tax-year period.
Contact us for more details about this opportunity to get hefty tax write-offs if you buy a heavy SUV for business.
© 2023
With a recession on the horizon – or already here, depending on who you talk to – employees are feeling the sting of inflation, and employers are feeling the financial pinch from decreased consumer buying power and increased caution in spending. Traditionally, layoffs are one of the first options to save money, which harms productivity and employee morale in the long run. In today’s economic climate and tight labor market, CFOs have much to consider and a unique opportunity.
Americans are awful at using vacation hours. Even with lucrative time off policies, paid time off (PTO) hours can sit in a bank waiting to be used or cashed in when an employee leaves the company. The standard has been a tiered benefits package based on years of service with the organization. While the quality depends on the package, what’s true across the board is not every person will use every benefit. According to recent studies, women and persons of color are far less likely to use all their PTO. Furthermore, female team members are more likely to value an emergency fund than their male counterparts. Translation: your company is probably paying for benefits your employees may not use or value.
More and more companies are using convertible benefits to create flexibility and increase utilization, maximizing the employees’ value and balancing company’s cost.
Convertible benefits increase employee satisfaction. Approximately 80% of employees are not actively engaged, costing the company funds in productivity waste and increasing the likelihood of turnover.
Convertible benefits create an inclusive and attractive work culture. When recruiting new team members, studies show a diverse workforce is a key factor for many job seekers. A flexible benefits package can help attract talent from a range of backgrounds.
A convertible benefit program does not have to be complex. Employees should be able to use their PTO or trade it in for cash contributed to a retirement account or money to create an emergency fund. Younger team members may want to convert unused PTO into payments toward their student loans. The goal is to give the team options, listen to their feedback, and adjust where you can. For assistance reviewing your human capital costs and ideas on avoiding layoffs and salary reductions, please get in touch with our trusted team of professionals.
Many people began working from home during the COVID-19 pandemic — and many still work from their home offices either all the time or on a hybrid basis. If you’re self-employed and run your business from home or perform certain functions there, you might be able to claim deductions for home office expenses against your business income. There are two methods for claiming this tax break: the actual expense method and the simplified method.
In general, you qualify for home office deductions if part of your home is used “regularly and exclusively” as your principal place of business.
If your home isn’t your principal place of business, you may still be able to deduct home office expenses if:
Many eligible taxpayers deduct actual expenses when they claim home office deductions. Deductible home office expenses may include:
But keeping track of actual expenses can take time and it requires organized recordkeeping.
Fortunately, there’s a simplified method: You can deduct $5 for each square foot of home office space, up to a maximum of $1,500.
The cap can make the simplified method less valuable for larger home office spaces. Even for small spaces, taxpayers may qualify for bigger deductions using the actual expense method. So, tracking your actual expenses can be worth it.
When claiming home office deductions, you’re not stuck with a particular method. For instance, you might choose the actual expense method on your 2022 return, use the simplified method when you file your 2023 return next year and then switch back to the actual expense method for 2024. The choice is yours.
If you sell — at a profit — a home on which you claimed home office deductions, there may be tax implications. We can explain them to you.
Also be aware that the amount of your home office deductions is subject to limitations based on the income attributable to your use of the office. Other rules and limitations may apply. But any home office expenses that can’t be deducted because of these limitations can be carried over and deducted in later years.
Unfortunately, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act suspended the business use of home office deductions from 2018 through 2025 for employees. Those who receive paychecks or Form W-2s aren’t eligible for deductions, even if they’re currently working from home because their employers closed their offices due to COVID-19.
We can help you determine if you’re eligible for home office deductions and how to proceed in your situation.
© 2023
Merger and acquisition activity dropped dramatically last year due to rising interest rates and a slowing economy. The total value of M&A transactions in North America in 2022 was down 41.4% from 2021, according to S&P Global Market Intelligence.
But some analysts expect 2023 to see increased M&A activity in certain industries. If you’re considering buying or selling a business, it’s important to understand the tax implications.
Under current tax law, a transaction can basically be structured in two ways:
1. Stock (or ownership interest). A buyer can directly purchase a seller’s ownership interest if the target business is operated as a C or S corporation, a partnership, or a limited liability company (LLC) that’s treated as a partnership for tax purposes.
The current 21% corporate federal income tax rate makes buying the stock of a C corporation somewhat more attractive. That’s because the corporation will pay less tax and generate more after-tax income. Plus, any built-in gains from appreciated corporate assets will be taxed at a lower rate when they’re eventually sold.
The current individual federal tax rates have also made ownership interests in S corporations, partnerships, and LLCs more attractive. Reason: The passed-through income from these entities also is taxed at lower rates on a buyer’s personal tax return. However, individual rate cuts are scheduled to expire at the end of 2025.
2. Assets. A buyer can also purchase the assets of a business. This may happen if a buyer only wants specific assets or product lines. And it’s the only option if the target business is a sole proprietorship or a single-member LLC that’s treated as a sole proprietorship for tax purposes.
What buyers want
For several reasons, buyers usually prefer to buy assets rather than ownership interests. In general, a buyer’s primary goal is to generate enough cash flow from an acquired business to pay any acquisition debt and provide an acceptable return on the investment. Therefore, buyers are concerned about limiting exposure to undisclosed and unknown liabilities and minimizing taxes after a transaction closes.
A buyer can step up (or increase) the tax basis of purchased assets to reflect the purchase price. Stepped-up basis lowers taxable gains when certain assets, such as receivables and inventory, are sold or converted into cash. It also increases depreciation and amortization deductions for qualifying assets.
In general, sellers prefer stock sales for tax and nontax reasons. One of their objectives is to minimize the tax bill from a sale. That can usually be achieved by selling their ownership interests in a business (corporate stock, or partnership or LLC interests) as opposed to selling assets.
With a sale of stock or other ownership interest, liabilities generally transfer to the buyer, and any gain on sale is generally treated as lower-taxed long-term capital gain (assuming the ownership interest has been held for more than one year).
Be aware that other issues, such as employee benefits, can also cause tax issues in M&A transactions. Buying or selling a business may be the largest transaction you’ll ever make, so it’s important to seek professional assistance before finalizing a deal. After a transaction is complete, it may be too late to get the best tax results. Contact us about how to proceed.
© 2023
The IRS has released the updated tax brackets, deductions, and credits for the 2023 tax year. While tax filing for this year won’t happen until early 2024, it’s important to pay attention to your tax rate. Strategizing now can help minimize your tax liability and maximize your income potential. Here are the updated numbers for 2023.
The tax brackets for the 2023 tax year (filing in the spring of 2024) are as follows:
| Tax Rate | Single Filers, Married Filing Separately* | Heads of Household | Married Filing Jointly |
| 10% | < $11,000 | <$15,700 | < $22,000 |
| 12% | $11,000 | $15,700 | $22,000 |
| 22% | $44,725 | $59,850 | $89,450 |
| 24% | $95,375 | $95,350 | $190,750 |
| 32% | $182,100 | $182,100 | $364,200 |
| 35% | $231,250 | $231,250 | $462,500 |
| 37% | $578,125/$346,875* | $578,100 | $693,750 |
In addition to the tax brackets for 2023, taxpayers should be aware of these credits, deductions, and phase-outs.
To discuss how these updates may affect your unique tax situation or to create a tax plan for the year, please reach out to one of our knowledgeable professionals today!
A business owner’s plate is quite full, if not overflowing, from the day-to-day operations to the background necessities like marketing and financial activities. The reality is it’s difficult to do everything and be everyone for your business. Working with an outsourced Chief Financial Officer, or vCFO, could be the right move for your business in 2023, and here is why.
Time management is crucial to the success of a business. Trying to handle financial risk assessments, financial reporting, record keeping, and even financial planning often diverts time away from other critical tasks. A vCFO will use their expertise and resources to complete financial tasks quickly and accurately, allowing you to redirect hours to other business functions.
As a business owner, you know your product or service and all the nuances inside and out. Customers pay you for your product, service, and expertise. When you outsource a CFO, you will gain access to decision support, new ideas, and an experienced perspective.
A vCFO can help with decision-making, financial ratio, cost-benefit, and pricing analyses. Or they can provide an outside perspective on future business moves you’re considering and ask the hard questions you may be afraid to ask.
Hiring a full-time CFO is either cost prohibitive or unrealistic if there isn’t 40 hours’ worth of work. Outsourcing allows businesses to pay only for the hours and tasks they need allowing the business to save money.
Getting bogged down in the minute details of running a business can cause business owners to miss the bigger picture and make it harder to shift when the winds of change come blowing in. Outsourcing financial tasks to an expert frees up time for the business owner to step back and see what opportunities and roadblocks may lie ahead. They can also be a sounding board and provide insight into the different directions you are considering.
Maybe your business finances need to be straightened out, you need help making heads or tails of the numbers, or your business isn’t bringing in the revenue you’d expect even with new customers and increasing sales. Outsourced CFOs bring a wealth of experience to the table that helps business owners by providing expert guidance through these scenarios. And, if you need to raise capital or investigate business loans, the outsourced CFO can also assist with those tasks.
There will come a time when the right move is moving on from the business. This could mean retirement or finding new opportunities elsewhere. Experienced CFOs can guide you through the various options and help you select the options that align best with your goals.
Are you ready to discuss what an outsourced CFO can do for your business? Reach out to our knowledgeable professionals to set up a time to discuss your goals and how you plan to get there.
Many businesses in certain industries employ individuals who receive tips as part of their compensation. These businesses include restaurants, hotels, and salons.
Tips are optional payments that customers make to employees who perform services. They can be cash or noncash. Cash tips include those received directly from customers, electronically paid tips distributed to employees by employers, and tips received from other employees under tip-sharing arrangements. Generally, workers must report cash tips to their employers. Noncash tips are items of value other than cash. They may include tickets, passes, or other items that customers give employees. Workers don’t have to report noncash tips to employers.
For tax purposes, four factors determine whether a payment qualifies as a tip:
Tips can also be direct or indirect. A direct tip occurs when an employee receives it directly from a customer, even as part of a tip pool. Directly tipped employees include wait staff, bartenders and hairstylists. An indirect tip occurs when an employee who normally doesn’t receive tips receives one. Indirectly tipped employees include bussers, service bartenders, cooks and salon shampooers.
Tipped workers must keep daily records of the cash tips they receive. To keep track of them, they can use Form 4070A, Employee’s Daily Record of Tips. It is found in IRS Publication 1244.
Workers should also keep records of the dates and value of noncash tips. Although the IRS doesn’t require workers to report noncash tips to employers, they must report them on their tax returns.
Employees must report tips to employers by the 10th of the month following the month they were received. The IRS doesn’t require workers to use a particular form to report tips. However, a worker’s tip report generally should include:
Note: Employees whose monthly tips are less than $20 don’t need to report them to their employers but must include them as income on their tax returns.
Employers should send each employee a Form W-2 that includes reported tips. Employers also must:
In addition, “large” food or beverage establishments must file an annual report disclosing receipts and tips on Form 8027, Employer’s Annual Information Return of Tip Income and Allocated Tips.
If you’re an employer with tipped workers providing food and beverages, you may qualify for a federal tax credit involving the Social Security and Medicare taxes that you pay on employees’ tip income. The tip tax credit may be valuable to you. If you have any questions about the tax implications of tips, don’t hesitate to contact us.
© 2023
An array of tax-related limits that affect businesses are indexed annually, and due to high inflation, many have increased more than usual for 2023. Here are some that may be important to you and your business.
The amount of employees’ earnings that are subject to Social Security tax is capped for 2023 at $160,200 (up from $147,000 for 2022).
These are only some of the tax limits and deductions that may affect your business and additional rules may apply. Contact us if you have questions.
© 2023
With the 2023 filing season deadline drawing near, be aware that the deadline for businesses to file information returns for hired workers is even closer. By January 31, 2023, employers must file these forms:
Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement. W-2 forms show the wages paid and taxes withheld for the year for each employee. They must be provided to employees and filed with the Social Security Administration (SSA). The IRS notes that “because employees’ Social Security and Medicare benefits are computed based on information on Form W-2, it’s very important to prepare Form W-2 correctly and timely.”
Form W-3, Transmittal of Wage and Tax Statements. Anyone required to file Form W-2 must also file Form W-3 to transmit Copy A of Form W-2 to the SSA. The totals for amounts reported on related employment tax forms (Form 941, Form 943, Form 944 or Schedule H for the year) should agree with the amounts reported on Form W-3.
Failing to timely file or include the correct information on either the information return or statement may result in penalties.
The January 31 deadline also applies to Form 1099-NEC, Nonemployee Compensation. These forms are provided to recipients and filed with the IRS to report non-employee compensation to independent contractors.
Payers must complete Form 1099-NEC to report any payment of $600 or more to a recipient.
If the following four conditions are met, you must generally report payments as nonemployee compensation:
Your business may also have to file a Form 1099-MISC for each person to whom you made certain payments for rent, medical expenses, prizes and awards, attorney’s services and more.
If you have questions about filing Form W-2, Form 1099-NEC or any tax forms, contact us. We can assist you in staying in compliance with all rules.
© 2023
If your small business has a retirement plan, and even if it doesn’t, you may see changes and benefits from a new law. The Setting Every Community Up for Retirement Enhancement 2.0 Act (SECURE 2.0) was recently signed into law. Provisions in the law will kick in over several years.
SECURE 2.0 is meant to build on the original SECURE Act, which was signed into law in 2019. Here are some provisions that may affect your business.
Retirement plan automatic enrollment. Under the new law, 401(k) plans will be required to automatically enroll employees when they become eligible, beginning with plan years after December 31, 2024. Employees will be permitted to opt out. The initial automatic enrollment amount would be at least 3% but not more than 10%. Then, the amount would be increased by 1% each year thereafter until it reaches at least 10%, but not more than 15%. All current 401(k) plans are grandfathered. Certain small businesses would be exempt.
Part-time worker coverage. The first SECURE Act requires employers to allow long-term, part-time workers to participate in their 401(k) plans with a dual eligibility requirement (one year of service and at least 1,000 hours worked or three consecutive years of service with at least 500 hours worked). The new law will reduce the three-year rule to two years, beginning after December 31, 2024. This provision would also extend the long-term part-time coverage rules to 403(b) plans that are subject to ERISA.
Employees with student loan debt. The new law will allow an employer to make matching contributions to 401(k) and certain other retirement plans with respect to “qualified student loan payments.” This means that employees who can’t afford to save money for retirement because they’re repaying student loan debt can still receive matching contributions from their employers into retirement plans. This will take effect beginning after December 31, 2023.
“Starter” 401(k) plans. The new law will allow an employer that doesn’t sponsor a retirement plan to offer a starter 401(k) plan (or safe harbor 403(b) plan) that would require all employees to be default enrolled in the plan at a 3% to 15% of compensation deferral rate. The limit on annual deferrals would be the same as the IRA contribution limit with an additional $1,000 in catch-up contributions beginning at age 50. This provision takes effect beginning after December 31, 2023.
Tax credit for small employer pension plan start-up costs. The new law increases and makes several changes to the small employer pension plan start-up cost credit to incentivize businesses to establish retirement plans. This took effect for plan years after December 31, 2022.
Higher catch-up contributions for some participants. Currently, participants in certain retirement plans can make additional catch-up contributions if they’re age 50 or older. The catch-up contribution limit for 401(k) plans is $7,500 for 2023. SECURE 2.0 will increase the 401(k) catch-up contribution limit to the greater of $10,000 or 150% of the regular catch-up amount for individuals ages 60 through 63. The increased amounts will be indexed for inflation after December 31, 2025. This provision will take effect for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2024. (There will also be increased catch-up amounts for SIMPLE plans.)
Retirement savings for military spouses. SECURE 2.0 creates a new tax credit for eligible small employers for each military spouse that begins participating in their eligible defined contribution plan. This became effective in 2023.
These are only some of the provisions in SECURE 2.0. Contact us if you have any questions about your situation.
© 2023
Please join us in congratulating Kim Spinardi, Partner at Hamilton Tharp, for being named a 2023 Rising Aztec!
Kim is one of ten SDSU alumni to earn the biennial award, which recognizes up-and-coming alumni. Recipients of this prestigious accolade are young professionals with extraordinary career achievements who are also recognized for their support of SDSU and engagement with the University and community.
Kim is a passionate supporter of the Aztec community. She is an SDSU Alumni board member and part of the Intercollegiate athletics committee. Kim mentors students through the Aztec Mentor Program (AMP) and Aztecs Going Pro. Additionally, Kim supports the university through fundraising for campus initiatives, colleges, and student organizations.
We are proud to have Kim on our team and to support SDSU in recognizing the achievements of its alumni. Congratulations, Kim, for this remarkable recognition of your endeavors. Keep up your exemplary work! Learn more about Kim and the other SDSU Alumni 2023 Rising Aztecs.
The IRS recently released the 2023 mileage rates for businesses to use as guidance when reimbursing workers for applicable miles driven within the year. The rates tend to increase yearly to account for rising fuel and vehicle and maintenance costs and insurance rate increases.
Businesses can use the standard mileage rate to calculate the deductible costs of operating qualified automobiles for business, charitable, medical, or moving purposes. Keep reading for the updated mileage rates and some reminders for mileage reimbursements and deductions.
Standard mileage rates for cars, vans, and pickups or panel trucks are as follows:
| Use Category | Mileage rate (as of Jan. 1, 2023) | Change from the previous year |
| Business miles driven | $0.655 per mile | $0.03 increase from mid-year 2022 |
| Medical or moving miles driven* | $0.22 per mile | $0.00 increase from mid-year 2022 |
| Miles driven for charitable organizations | $0.14 per mile | Note: Only congress may adjust the mileage rate for service to a charitable organization by a Congress-passed statute. |
*Moving miles reimbursement for qualified active-duty members of the Armed Forces
When reimbursing employees for miles driven, keep the following in mind:
To review your organization’s mileage reimbursement policy and any alternate methods for calculating appropriate reimbursement amounts, reach out to our team of knowledgeable professionals today.
The Employee Retention Credit (ERC) was a valuable tax credit that helped employers that kept workers on staff during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. While the credit is no longer available, eligible employers that haven’t yet claimed it might still be able to do so by filing amended payroll returns for tax years 2020 and 2021.
However, the IRS is warning employers to beware of third parties that may be advising them to claim the ERC when they don’t qualify. Some third-party “ERC mills” are promising that they can get businesses a refund without knowing anything about the employers’ situations. They’re sending emails, letters and voice mails as well as advertising on television. When businesses respond, these ERC mills are claiming many improper write-offs related to taxpayer eligibility for — and computation of — the credit.
These third parties often charge large upfront fees or a fee that’s contingent on the amount of the refund. They may not inform taxpayers that wage deductions claimed on the companies’ federal income tax returns must be reduced by the amount of the credit.
According to the IRS, if a business filed an income tax return deducting qualified wages before it filed an employment tax return claiming the credit, the business should file an amended income tax return to correct any overstated wage deduction. Your tax advisor can assist with this.
Businesses are encouraged to be cautious of advertised schemes and direct solicitations promising tax savings that are too good to be true. Taxpayers are always responsible for the information reported on their tax returns. Improperly claiming the ERC could result in taxpayers being required to repay the credit along with penalties and interest.
The ERC is a refundable tax credit designed for businesses that:
Eligible taxpayers could have claimed the ERC on an original employment tax return or they can claim it on an amended return.
To be eligible for the ERC, employers must have:
As a reminder, only recovery startup businesses are eligible for the ERC in the fourth quarter of 2021. Additionally, for any quarter, eligible employers cannot claim the ERC on wages that were reported as payroll costs in obtaining Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) loan forgiveness or that were used to claim certain other tax credits.
If you didn’t claim the ERC, and believe you’re eligible, contact us. We can advise you on how to proceed.
© 2023
The new Secure Act 2.0 legislation expands upon the Secure Act of 2019 with updates to retirement savings plans across the country. Here’s what you need to know.
Plan sponsors of 401(k) and 403(b) plans will be required to automatically enroll eligible employees with a starting contribution of 3% of their salary beginning in 2025. This amount will increase annually by 1% until the deferral amount reaches 10% of their earnings. Employees can opt-out if they do not wish to enroll in the sponsored retirement plan. This goes into effect for all existing defined-contribution plans if the employer has more than 10 employees and has existed for more than three years. Government and churches are excluded.
In addition, unenrolled participant notification requirements have been eliminated except for an annual reminder of plan requirements and their opportunity to participate.
Over the next 10 years, the age when required minimum distributions go into effect will increase. Here are the highlights:
For those who failed to make their required minimum contribution, the Act reduces the penalty from 50% to 25%.
Certain hardships are eligible for penalty-free early withdrawals from retirement accounts, where retirement account owners are only responsible for applicable taxes instead of the early withdrawal fee. Eligible hardships have been expanded to include victims of domestic violence, terminally ill patients, and certain personal financial emergencies. In addition, victims of qualified federal disasters who have experienced significant financial impact may take an early withdrawal without penalty within 180 days of the disaster.
Currently, taxpayers aged 50 or older can make catch-up contributions to eligible retirement plans, like a 401(k) or IRA. Beginning in 2025, The Secure Act 2.0 increases limits to the greater of $10,000 or 50% more than the original catch-up amount for those aged 60, 61, 62, or 63. In addition, IRA catch-up limits will no longer be set to $1,000 per year but will increase with inflation. In 2024, catch-up contributions will also be subject to after-tax (ROTH) rules.
The Secure Act 2.0 permits qualified 403(b) and governmental 457(b) plans to allow employees to designate employer matching, nonelective contributions, and student loan matching contributions as pre- or post-tax contributions. Take note that Roth-designated employer contributions must be 100% vested.
If a part-time worker has worked for an employer for at least three consecutive years and worked a minimum of 500 hours per year for those three years, the plan sponsor must allow them to contribute to qualified 401(k) plans. Effective for 401(k) and 403 (b) plans beginning after December 31, 2024, the three-year requirement has been reduced to two years.
Beginning in 2023, businesses with 50 employees or fewer can take a credit of up to 100% of the startup costs for workplace retirement plans, up to the annual cap of $5,000. This is an increase from the 50% credit previously offered.
To review how your tax strategy is affected by the Secure Act 2.0, reach out to our team of knowledgeable professionals.
If you’re considering converting your C corporation to an S corporation, be aware that there may be tax implications if you’ve been using the last in, first out (LIFO) inventory method. That’s because of the LIFO recapture income that will be triggered by converting to S corporation status. We can meet to compute what the tax on this recapture would be and to see what planning steps might be taken to minimize it.
As you’re aware, your corporation has been reporting a lower amount of taxable income under LIFO than it would have under the first in, first out (FIFO) method. The reason: The inventory taken into account in calculating the cost of goods sold under LIFO reflects current costs, which are usually higher.
This benefit of LIFO over FIFO is equal to the difference between the LIFO value of inventory and the higher value it would have had if the FIFO method had been used. In effect, the tax law treats this difference as though it were profit earned while the corporation was a C corporation. To make sure there’s a corporate-level tax on this amount, it must be “recaptured” into income when the corporation converts from a C corporation to an S corporation. Also, the recapture amount will increase the corporation’s earnings and profits, which can have adverse tax consequences down the road.
There are a couple of rules that soften the blow of this recapture tax to some degree.
We can help you gauge your exposure to the LIFO recapture tax and can suggest strategies for reducing it. Contact us to discuss these issues in detail.
© 2022